Stomata
Stomata: Overview
In this topic, we will learn about stomata and their significant features. It discusses the structure and functions of stomata with the aid of diagrams.
Important Questions on Stomata
Mention the role of abscisic acid in stomatal closure.
Match the column-I with column-II and select the correct combination.
| Column-I | Column-II | ||
| Bulliform cells | Hydathodes | ||
| Subsidiary cells | Isobilateral leaf | ||
| Epithem | Stomata | ||
| Cork cells | Phellem |
Which of the following cells play an important role in the transpiration other than guard cells?
Explain the location of subsidiary cells in the body of a plant.
Which cells are present in the region of next to guard cells in the body of a plant? (subsidiary cells/parenchyma cells)
Explain the role of subsidiary cells in transpiration.
Subsidiary cells have no role in the stomatal transpiration.
The specialised plant cells present in the epidermis of the leaves, surrounding the stomata are called_____cells.
Given below is a diagram of the stomatal apparatus. Match the labels with the corresponding names of the compounds.
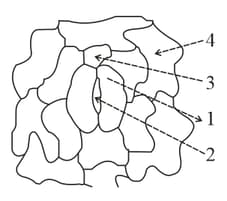
Choose the correct combination.
Red light is more effective than blue light in opening the stomatal pore. Yes or no? If no, correct the statement.
Which of the following amphistomatous leaves would dry up last?
The following figure shows the stomatal apparatus. Identify the parts labeled as A, B, C and D. Choose the correct answer from the following
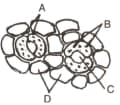
Water is lost from the leaves by the transpiration process through _____.
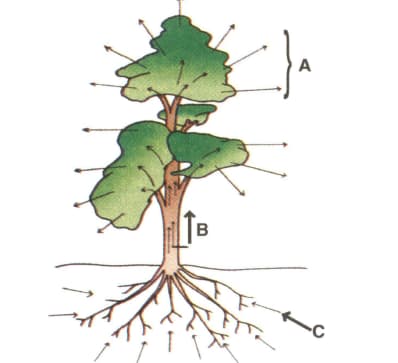
An outline sketch of a tree is shown in a diagram below. Study the name and answer questions that follows
________ are the specialized epidermal cells surrounding guard cells.
The metal ion involved in the stomatal regulation or stomata opening. There is accumulation of the following element in the guard cells ______ during stomatal movement.
Which of the following facilitates opening of stomatal aperture?
