Microscopic Anatomy of Testis and Ovary
Microscopic Anatomy of Testis and Ovary: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as Ovarian Follicles, Germinal Epithelium, Testicular Lobules, Seminiferous Tubules, Sertoli Cells, Leydig Cells, Primary Follicle, Zona Pellucida, Graafian follicle, Corona Radiata, Secondary Follicles, etc.
Important Questions on Microscopic Anatomy of Testis and Ovary
Cells that produce testosterone in the presence of luteinizing hormone (LH) are:
Choose the correct option to label the region .
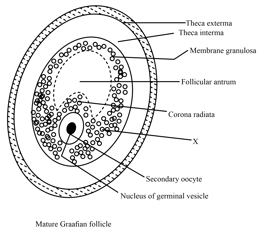
The diagram given below is representing:
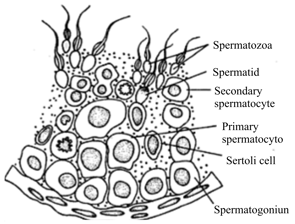
The secondary follicles are arrested at prophase I before sexual maturity.
Fill in the blank with the correct option provided in the bracket.
The secondary follicle is formed after the completion of the _____ (first meiotic/second meiotic/mitotic) division of primary follicle
The secondary follicle is formed after the completion of the first meiotic division of the primary follicle.
The secondary follicle is formed after
How secondary follicle inside the human female ovary is formed?
The surrounding granulosa cells is called the _____.(cumulus oophorus/corona radiata)
Secondary follicles consist of many layers of cuboidal cells known as membrane granulosa cells.
The follicle is surrounded by the theca interna, whose cells produce _____.(hormones/enzymes)
Explain follicular development?
The secondary follicles look very similar to primary follicles.
Follicular atresia was accompanied by the appearance of _____. (epithelial nest/connective tissue)
Follicular atresia is a normal process in the ovary to regulate the number of follicles in the developing pool.
Define liquor folliculi.
Follicular atresia is the breakdown of the ovarian follicles, which consist of an oocyte surrounded by _____.
Define tunica albuginea?
Define visceral peritoneum?
Define germinal (ovarian) epithelium?
