Male Reproductive System
Male Reproductive System: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Scrotum, Rete testis, Penis & Male Accessory Glands etc.
Important Questions on Male Reproductive System
The diagram given below is representing:
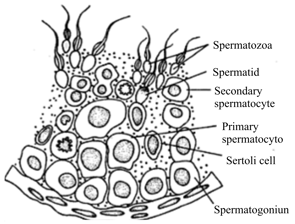
Choose the correct option.
Each testicular lobule contains _____ convoluted seminiferous tubules.
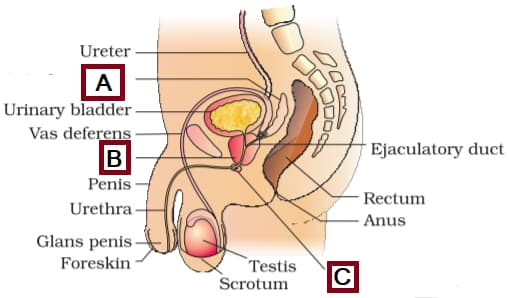
Urethral meatus refers to the:
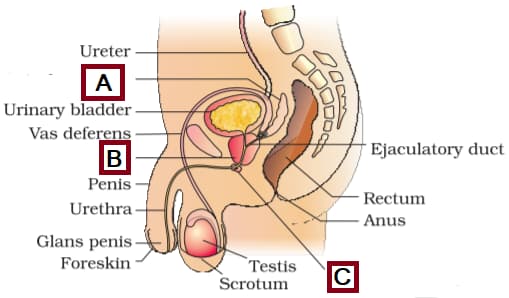
Given below is a diagrammatic sketch of a portion of the human male reproductive system.
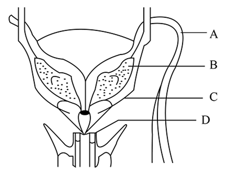
A network of tubules in the hilum of the testicles are called
Fill in the blank with the correct answer from the bracket.
_____ connects seminiferous tubules to the vasa efferentia. (Rete testis, Epididymis, vasa deferentia)
A network of tubules in the hilum of the testicles are called
The rete testis connects seminiferous tubules to the efferent ducts.
Write a short note on rete testis.
Name the tubule that connects rete testis to the epididymis, whether it is vasa deferentia or vasa efferentia?
Write a short note on vasa efferentia.
Vasa efferentia connects epididymis to vasa deferentia.
The tubule that helps the transportation of sperms from rete testis to the epididymis is called
Presence of ________ is an indication of abdominal origin of testis.
Testis acts as only an exocrine gland.
The seminiferous tubule is covered by corona radiata.
The yellowish and sticky secretion from the seminal vesicle contains
Each testis is divided into how many testicular lobules.
Human testes are found in scrotal sacs and outside the abdominal cavity because the maturation of sperms requires 2oC-2.5oC less than body temperature.
The secretion of which gland activates sperms and prevents coagulation of semen. (Answer in a single word)
The fructose present in the secretion of the seminal vesicle provides energy to the sperm in the form of
