Seed and Fruit Formation
Seed and Fruit Formation: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as Seed of a Plant, Seed Coat, Albuminous Seed, Non-Albuminous Seed, Perisperm, Dormancy, Fruit, Types of Fruit, False Fruit, True Fruit, Parthenocarpy, and Advantages of Seed.
Important Questions on Seed and Fruit Formation
Seeds that possess a special food storage tissue called the endosperm are said to be:
Which of the following are examples of parthenocarpy?
Phoenix dactylifera is an example of -------------------------.
Perisperm is
Parthenogenesis is
Plumule, epicotyl, and hypocotyl are:
Identify and in this figure.
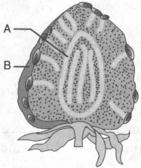
The root cap of monocot is covered in
Endosperm is completely consumed during seed formation in
Fruit develops from
Which of the following is an example of dry fruit?
Example of false fruit
All are examples of albuminous seeds except
Identify the incorrect statement about parthenocarpy.
Protective layer of the radicle during seed germination and endosperm formation is:
Identify the wrong statement regarding post-fertilization development:
Identify the correct match for the Maize grain from the given options
Perisperm present in the seeds of:
Respiratory exchange in seeds occur through
By hormone application it is possible to obtain seedless fruits. In which of the following it is undesirable to obtain seedless fruits
