Plant Tissues
Plant Tissues: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Anatomy of Flowering Plants, Plant Tissue, Phloem Fibres & Phloem Parenchyma etc.
Important Questions on Plant Tissues
Cambium of root is an example of:
In the sieve elements, which one of the following is the most likely function of P-proteins?
Companion cells in plants are associated with:
In a dicotyledonous stem, the sequence of tissues from the outside to the inside is
Which of the following is enucleate at maturity?
Study the flow chart given below.
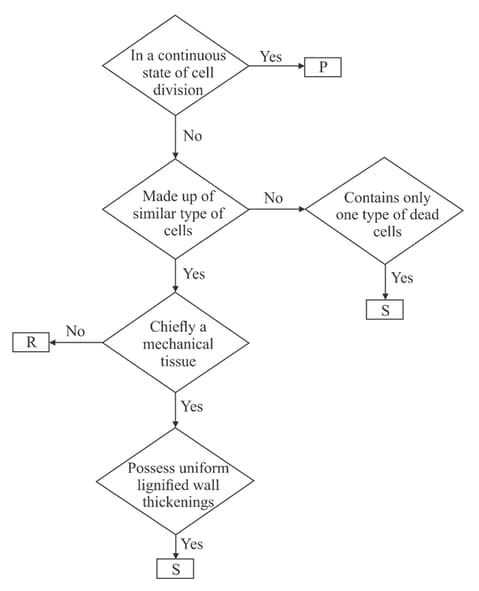
Which of the following statements is incorrect regarding this?
Assertion: Xylem and phloem lose their power of dividing and attain maturation.
Reason: These are complex permanent tissues.
Phloem is involved in the transport of water in plants.
Describe briefly about the parenchyma cells.
Husk of a coconut. It is made of sclerenchymatous tissue.
This process of taking up a permanent shape, size, and function by meristematic cells is called _____.
Mention the different types of permanent tissues.
The three ground tissues are parenchyma, collenchyma, and sclerenchyma.
In stems and roots, ground tissues are located in the _____ and pith.
Metaxylem is the part of _____ (primary/secondary) xylem in the plant.
Which of the following is responsible for the conduction of water in the body of a plant?
