Isomerism in Coordination Compounds
Isomerism in Coordination Compounds: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Isomerism in Coordination Compounds, Structural Isomerism, Geometrical Isomerism with Two Different Unidentate Ligands & Structures of Geometrical and Optical Isomers etc.
Important Questions on Isomerism in Coordination Compounds
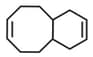
Number of geometrical isomer of given compound will be:
Among the following, a pair of resolvable configurational enantiomers is given by:
How many minimum no. of C-atoms are required for position and geometrical isomerism in alkene?
Which of the following compounds does exhibit stereoisomerism?
Which of the following has largest number of isomers?
(R is alkyl group, en is ethylediamine).
Geometrical isomerism is possible in?
Why is geometrical isomerism not possible in tetrahedral complexes having two different types of undentate ligands coordinated with the central metal ion?
Identify the isomer occur in the given ligand. _____ (Facial (fac) isomer/ Meridional (mer) isomer)
Define Facial (fac) isomer.
If three donor atoms of the same ligands occupy adjacent positions at the corners of an octahedral face, we have the facial (fac) isomer.
State the method to draw the different geometrical forms for a particular complex in octahedral geometry.
State the method to draw the different geometrical forms for a particular complex in square planer geometry.
_____ planar complexes do not show optical isomerism.
Square planar complexes show optical isomerism.
What is coordination isomerism in coordination compounds ?
What is Structural isomerism How is it classified?
Due to the presence of ambidentate ligands coordination compounds show isomerism. Palladium complexes of the type and are _____(linkage isomers/ionisation isomers)
Number of stereoisomers possible for the octahedral complexes and respectively, are:
[-ethylenediamine]
A metal complex having composition , was isolated in two forms and ( is bromine and is iodine).
(a) reacts with and gives a pale yellow precipitate which is insoluble in .
(b) reacts with and gives a yellow precipitate which is insoluble in .
The octahedral complex exists in two isomeric forms and . Isomer reacts with to give a white precipitate, but does not react with . Isomer gives white precipitate with but does not react with
