Versatile Nature of Carbon
Versatile Nature of Carbon: Overview
This topic describes the versatile property of carbon. It explains that catenation is the property by which an atom links to another atom of the same element. It also mentions that carbon has a high catenation tendency due to strong covalent bonds.
Important Questions on Versatile Nature of Carbon
Alkenes and alkynes are
Which of the following properties is not true regarding organic compounds.
How many structural isomers of heptane exist?
The melting and boiling points of hydrocarbons are determined by:
Solve the puzzle.
ACROSS:
6. Long chains of repeating molecules.
8. Organic group such as sugars and starches.
9. Compound with same empirical but different structural formula.
11. Large polymers of amino acids.
12. Hydrocarbon containing single bonds.
13. Hydrocarbon containing double bonds.
DOWN:
1. Term that refers to compounds with double and triple bonds.
2. Distillation used to separate petroleum into individual products.
3. Containing only hydrogen and carbon.
4. Plastic derived from petroleum.
5. Compounds containing the benzene ring.
7. Hydrocarbon containing triple bonds.
10. Alcohol often obtained from corn.
Draw the structure for the given compound.
2-Methyl-2-pentene
Name the compound according to the IUPAC system.
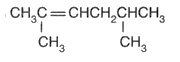
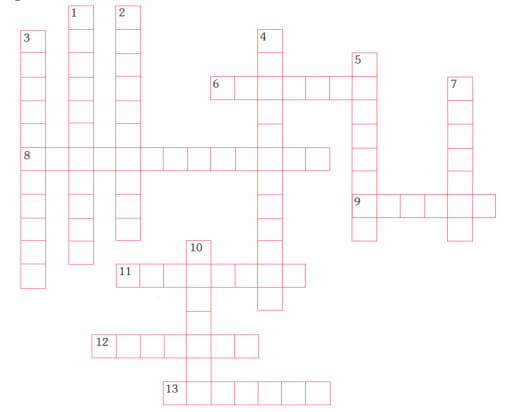
Name the compound according to the IUPAC system.
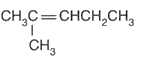
Name the compound according to the IUPAC system.
Name the compound according to the IUPAC system.
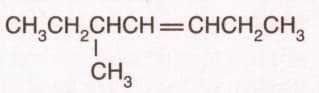
Name the compound according to the IUPAC system.
Define isomers.
Name the alkane which has three carbon atoms.
What are the differences between saturated and unsaturated compounds?
Draw the electron dot structure of .
What are the different types of covalent bonds found in carbons compounds? Briefly explain with examples.
Give three reasons for the existence of a large number of carbon compounds.
