Conductance in Electrolytic Solutions
Important Questions on Conductance in Electrolytic Solutions
is added to of saturated solution of . The conductivity of this solution at is .
[Given : at
The resistivity of a solution of an electrolyte is . Its molar conductivity is . (Nearest integer)
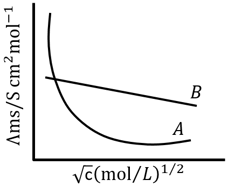
Following figure shows dependence of molar conductance of two electrolytes on concentration. is the limiting molar conductivity.
The number of Incorrect statement(s) from the following is _____
(A) for electrolyte is obtained by extrapolation
(B) For electrolyte graph is a straight line with intercept equal to
(C) At infinite dilution, the value of degree of dissociation approach zero for electrolyte .
(D) for any electrolyte or can be calculated using for individual ions.
Choose the correct representation of conductometric titration of benzoic acid vs sodium hydroxide.
Resistance of a conductivity cell (cell constant ) filled with solution of is (labelled as solution ). When the same cell is filled with solution of , the resistance is (labelled as solution ). The ratio of molar conductivity of solution and solution is i.e. . The value of is____Given, molar mass of is )
The molar conductivity of a conductivity cell filled with moles of solution is and that of moles another identical cell heaving solution is , The conductivities exhibited by these two cells are same.
The relationship between and is
Given below are two statements:
Statement I: For , molar conductivity increases steeply with dilution.
Statement II: For carbonic acid, molar conductivity increases slowly with dilution. In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below
The solubility product of a sparingly soluble salt is . If specific conductance of the solution is , the limiting molar conductivity of the solution is . The value of is:
The resistance of a conductivity cell containing solution at is . If the conductivity of solution at
is , then the cell constant of the conductivity cell is____
The resistance of conductivity cell with cell constant , containing at is . The molar conductivity of solution at in is (Integer answer)
Match List - I with List - II :
| List - I (Parameter) |
List - II (Unit) | ||
| (a) | Cell constant | (i) | |
| (b) | Molar conductivity | (ii) | Dimensionless |
| (c) | Conductivity | (iii) | |
| (d) | Degree of dissociation of electrolyte | (iv) |
Given below are two statements:
Statement I : The limiting molar conductivity of (strong electrolyte) is higher compared to that of $\mathrm{CH}_{3} \mathrm{COOH}$ (weak electrolyte).
Statement II : Molar conductivity decreases with decrease in concentration of electrolyte.
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
The conductivity of a weak acid of concentration is . If the ionization constant of is equal to
(Round off to the Nearest Integer)
A aqueous solution of has a conductance of when measured in a cell constant . The molar conductivity of this solution is _______ . (Round off to the Nearest Integer)
A solution of conductivity shows a resistance of in a conductivity cell. If the same cell is filled with an solution, the resistance drops to . The conductivity of the HCl solution is ____. (Round off to the Nearest Integer).
The molar conductivity at infinite dilution of barium chloride, sulphuric arid and hydrochloric acid are respectively. The molar conductivity at infinite dilution of barium sulphate is ___ ( Round off to the Nearest Integer).
The variation of molar conductively with concentration of an electrolyte (X) in aqueous solution is shown in the given figure.
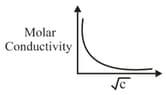
The electrolyte X is :
Which one of the following graphs between molar conductivity versus is correct?
Consider the statements and :
: Conductivity always increases with decreases in the concentration of electrolyte.
: Molar conductivity always increases with decreases in the concentration of electrolyte.
The correct option among the following
The equivalent conductance of at concentration C and at infinite dilution are and , respectively. The correct relationship between and is given as :
(where the constant B is positive)