Advantages of the Long Form of the Periodic Table in Learning Chemistry
Advantages of the Long Form of the Periodic Table in Learning Chemistry: Overview
This topic lists some of the advantages of long form of the periodic table for students and scholars of chemistry. It explains how this periodic table helps us understand the elements, compounds and the reactions between them.
Important Questions on Advantages of the Long Form of the Periodic Table in Learning Chemistry
Which of the following are the characteristics of isotopes of an element?
Isotopes of an element have same atomic masses.
Isotopes of an element have same atomic number.
Isotopes of an element show same physical properties.
Isotopes of an element show same chemical properties.
Which one of the following does not increase while moving down the group of the periodic table?
Which one of the following depict the correct representation of atomic radius(r) of an atom?
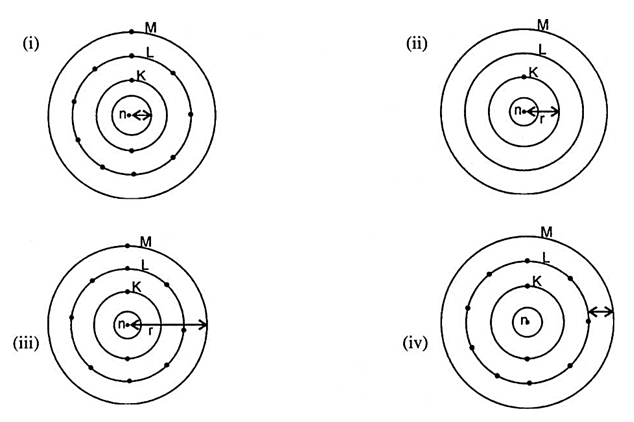
The element with atomic number 14 is hard and forms an acidic oxide and a covalent halide. To which of the following categories does the element belong?
Which of the following statements is not correct about the trends when going from left to right across the long form of the period table?
On the basis of Mendeleev's periodic table given below, answer the questions that follow the table:
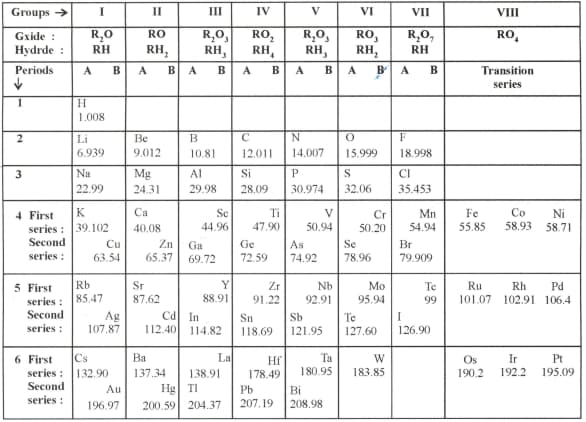
(a) Name the elements that is in
(i) 1st group and 3rd period
(ii) VIIth group and 2nd period
(b) Suggest the formula for the following:
(i) oxide of nitrogen (ii) hydride of oxygen
(c) In group VIII of the periodic table, why does cobalt with atomic mass 58.93 appear before nickel having atomic mass 58.71?
(d) Besides gallium, which other two elements have since been discovered for which Mendeleev had left gaps in his periodic table?
(e) Using atomic masses of Li, Na and K, find the average masses of Li and K and compare it with the atomic mass of Na. State the conclusion drawn from this activity.
Write the formula of the product formed when element A (atomic number 19) combines with element B (atomic number 17). Draw its electronic dot structure. What is the nature of the bond formed?
Identify the elements with the following property and arrange them in the increasing order of their reactivity.
(a) An element that is a soft and reactive metal
(b) The metal that is an important constituent of limestone
(c) The metal that exists in the liquid state at room temperature
The position of three elements A, B and C in the periodic table are shown below:
Group VI | Group VII |
|---|---|
| - | - |
| - | A |
| - | - |
| B | C |
Giving reasons, for the following:
(a) Element A is a non metal.
(b) Element B has a larger atomic size than element C.
(c) Element C has a valency of 1.
How will the tendency to gain electrons changes as we go from left to right across a period and why?
Why do all elements in a same group have similar properties?
What is meant by periodicity in properties of elements with reference to the periodic table.
| H | He | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Li | Be | B | C | N | O | F | Ne | |
| Na | Mg | Al | Si | P | S | CI | Ar |
Using the above table explains why:
(i) and are considered as active metals.
(ii) Atomic size of magnesium is less than sodium.
(iii) Fluorine is more reactive than chlorine.
Three elements A, B and C have 3, 4 and 2 electrons respectively in their outermost shell. Give the group number to which they belong in the modern periodic table. Also, give their valencies.
The elements of the second period of the periodic table are given below:
(a) Give reason to explain why atomic radii decreases from to .
(b) Identify the most (i) metallic and (ii) non-metallic element.
Two elements M and N belong to groups I and II respectively and are in the same period of the periodic table. How do the following properties of M and N vary?
(i) Sizes of their atoms (ii) Their metallic characters
(iii) Their valencies in forming oxides (iv) Molecular formulae of their chlorides
The elements of the third period of the periodic table are given below:
| Group | I | II | III | IV | V | VI | VII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Period 3 |
(a) Which atom is bigger, or ? Why?
(b) Identify the most (i) metallic and (ii) nonmetallic elements in period 3.
How many valence electrons are present in Eka-aluminium and Eka-silicon?
Arrange the following elements in the increasing order of their atomic radii.
Write the formulae of chlorides of Eka-silicon and Eka- aluminium, the elements predicted by Mendeleev.
