Gaseous Laws and Ideal Gas Equation
Important Questions on Gaseous Laws and Ideal Gas Equation
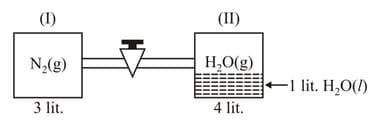
Two containers are connected by a tube of negligible volume, container has gas at pressure atm and temperature and container has litre at temperature initially. Find correct option(s) after stopcock is removed. (aq. Tension torr)
One mole of is taken in litre empty container fitted with a movable piston at If it is heated to at constant pressure then match the change (List) in parameters (List ) of gas as compared to initial state select the correct code.
| List (Parameter) | List (Change) | ||
| (number of collision made by a molecule per unit time) | |||
| (collision frequency) | |||
| (mean free path) | |||
| (root mean square speed) | |||
Which of the following curves does not represent Boyle's law:
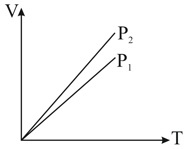
us curves at constant and for an ideal gas are shown in figure. Which is correct :
A hydrocarbon contains of carbon per of . One litre vapours of hydrocarbon at and atm pressure weighs . The molecular formula of hydrocarbon is :
One molecule of haemoglobin will combine with four molecules of oxygen. If of haemoglobin combines with of at body temperature and a pressure of , what is the molar mass of haemoglobin?
If the answer is of type , report the value of correct up to nearest integer.
A sample of natural gas is of methane () and of ethane () by mass. What would be the density of this mixture at and ?
Answer by rounding off up to two places of decimals.
The vapour pressure of water at is . Calculate the mass of water (in mg) per litre of air at and relative humidity.
Answer correct up to two places of decimals.
After of carbon reacts with oxygen originally occupying at and , the cooled gases are passed through of solution. Determine the concentration of remaining in the solution which is not converted to
[Note: does not react with under these conditions.]Assume that the centre of the sun consists of gases whose average molecular weight is . The density and pressure of the gases are and , respectively. Find the temperature. If then is:
A certain quantity of a gas occupied when collected over water at and pressure. If the dry gas occupies at , calculate the aqueous tension (in ) at .
A volume of a gas weighing was allowed to expand at a constant temperature until the pressure of the gas reduced to one-half of its former value. It was found that of the gas weighed . Determine the initial density of the gas in .
Mercury diffusion pumps may be used in the laboratory to produce a high vacuum. Cold traps are generally placed between the pump and the system to be evacuated. These cause the condensation of vapours, and prevent mercury from diffusing back into the system. The maximum pressure of mercury that can exist in the system is the vapour pressure of mercury at the temperature of the cold trap. Calculate the number of mercury-vapour molecules per present in a cold trap maintained at . The vapour pressure of mercury at this temperature is . If answer is report .
A glass tube sealed at both the ends is long. It lies horizontally with the mid containing . The two ends of the tube contain air at a temperature of and a pressure . The air column on one side is maintained at and on the other side. Calculate the length of the air column on the cooler side. Neglect the changes in the volume of mercury and of the glass.
Equation of Boyle's law is

