Chemical Properties of Carboxylic Acids
Chemical Properties of Carboxylic Acids: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Chemical Properties of Carboxylic Acids, Reactions of Carboxylic Acids involving Cleavage of O-H Bond, Reduction of Carboxylic Acids & Decarboxylation of Carboxylic Acids etc.
Important Questions on Chemical Properties of Carboxylic Acids
The IUPAC name of the following is
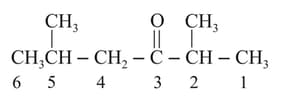
The Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky reaction is used to
When chlorine is passed through acetic acid in presence of halogen carrier (red ), it forms
Write the equation for the alkylation of carboxylic acids?
Explain the mechanism of alkylation of carboxylic acids?
At what position of carboxylic acids does alkylation take place?
The carboxylic acid reacts with sodium hydroxide produces sodium salt of acid.
The product of the reaction of carboxylic acid and sodium hydroxide can undergo decarboxylation. Write the chemical reaction of soda lime decarboxylation.
Give the product obtained when benzoic acid reacts with sodium hydroxide.
Which is the strongest acid?
Which of the following can undergo Ring substitution?
Aromatic carboxylic acids undergo electrophilic substitution reactions in which the ______ group acts as a deactivating and meta-directing group.
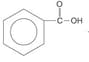
What is the above reaction?
Decarboxylation is the loss of the acid functional group as carbon dioxide from a carboxylic acid.
Describe Fischer esterification reaction.
The simplest method of preparation of esters is the _____
_____ are compounds formed by the reaction of carboxylic acids with alcohols.
In HVZ reaction substitution takes place at:
Which of the following will not undergo Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky reaction?
Arrange the following acids in their increasing order of acidic strength.
Acetic acid, chloroacetic acid, propionic acid, formic acid.
