Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Importance of Carbohydrates, Carbohydrates, Reaction of Glucose with Phenyl Hydrazine & Mutarotation etc.
Important Questions on Carbohydrates
The products obtained on hydrolysis of sucrose are:
The simplest carbohydrates which cannot be hydrolysed to smaller molecules are known as
Which of the following carbohydrate is a reducing sugar?
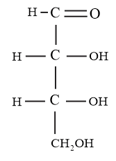
What are the products formed when -glucose is reacted with the following species?
(i)
(ii) Bromine water
Which of the following reactions and facts of D-glucose cannot be explained by its open chain structure?
(i) Despite having the aldehyde group, glucose does not give Schiff test and 2, 4-DNP test.
(ii) Glucose does not react with sodium hydrogen sulphite to form addition product.
(iii) The pentaacetate of glucose does not react with hydroxyl amine showing the absence of free-CHO group.
The Glycosidic linkages and Peptide linkages are present in:
Which of the following statements are true about carbohydrates?
Monosaccharides can be hydrolysed.
The two monosaccharide units obtained on hydrolysis of a disaccharide can either be same or different.
Polysaccharides are not sweet in taste.
All monosaccharides are not reducing sugars.
Synthesis of each molecule of glucose in photosynthesis involves
Among the following, the incorrect statement is
A disaccharide consisting of two glucose units in which of one glucose is linked to of another glucose unit is
Glycogen is branched chain polymer of glucose units in which chain is formed by glycosidic linkage where branching occurs by formation of glycosidic linkage. Structure of glycogen is similar to
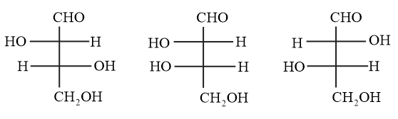
The corresponding order of names of four aldoses with configuration given below, respectively is: