Glucose and its Properties
Glucose and its Properties: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Preparation of Glucose from Sucrose (Cane Sugar), Preparation of Glucose from Starch, Mutarotation & Lobry de Bruyn van Ekenstein Rearrangement etc.
Important Questions on Glucose and its Properties
The products obtained on hydrolysis of sucrose are:
What are the products formed when -glucose is reacted with the following species?
(i)
(ii) Bromine water
Which of the following reactions and facts of D-glucose cannot be explained by its open chain structure?
(i) Despite having the aldehyde group, glucose does not give Schiff test and 2, 4-DNP test.
(ii) Glucose does not react with sodium hydrogen sulphite to form addition product.
(iii) The pentaacetate of glucose does not react with hydroxyl amine showing the absence of free-CHO group.
Name the reagent and condition required for carrying out of the following reaction
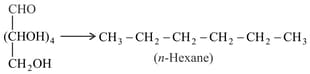
Treatment of -glucose with aqueous results in a mixture of monosaccharides, which are
Starch is hydrolysed in presence of sulphuric acid to obtain _____.
How is glucose obtained from starch?
Which of the following will form the same osazone when treated with excess of phenylhydrazine?
Glucose on treatment with excess of phenyl hydrazine gives
The products and respectively are
Name of the product formed when glucose reacts with concentrated .
Name the reagent which on reaction with glucose confirms the presence of five hydroxyl groups in glucose:
Total number of atoms in ring of pyranose are:
Glucose on reduction with gives
The beta and alpha glucose have different specific rotation. When either is dissolved in water, their specific rotation changed to reach a certain fixed value. This is called :-
How many of the following will produce gluconic acid or it's salt when treated with Glucose
(a) Tollen's reagent
(b)
(c) water
(d)
(e) Fehling's solution
(f) Red
(g) Benedict's solution
(h)
(i)
The _____ form of glucose is optically inactive.
Draw mirror images of glucose and fructose.
