Proteins
Proteins: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Proteins, Structure of Proteins, Denaturation of Proteins, Primary Structure of Proteins, Secondary Structure of Proteins, Tertiary Structure of Proteins, Quaternary Structure of Protein and, Polypeptides
Important Questions on Proteins
Carbon combines with nitrogen in amino acid linkages to form:
The following terms are associated with which of the following biomolecule:
(i) Primary structure
(ii) Denaturation
The following terms are associated with which of the following biomolecule:
(i) Primary structure
(ii) Denaturation
The naturally occurring amino acid that contains only one basic functional group in its chemical structure is
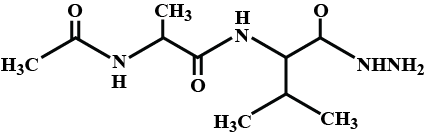
In an oligopeptide named Alanylglycylphenyl alanyl isoleucine, the number of hybridised carbons is _____.
The one that does not stabilize and structures of proteins is
Sulphur (S) containing amino acids from the following are:
(a) isoleucine
(b) cysteine
(c) lysine
(d) methionine
(e) glutamic acid
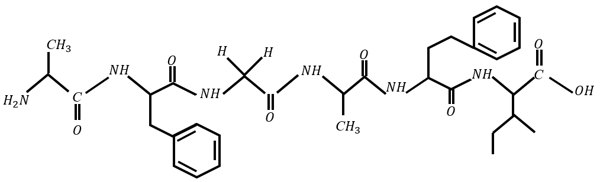
The number of hybridised carbon atoms in the following peptide is :
Ala-Phe-Gly-Ala-Phe-Leu
One which does not stabilise secondary and tertiary protein.
During protein synthesis in cells, amino acids condense (in the presence of enzymes) through the formation of the amide link , or peptide bond, to form a polypeptide chain, which then folds to form a biologically active protein. The equation below shows the formation of a dipeptide, Ala-Gly, formed by condensation of the two amino acids, alanine and glycine in a test tube.
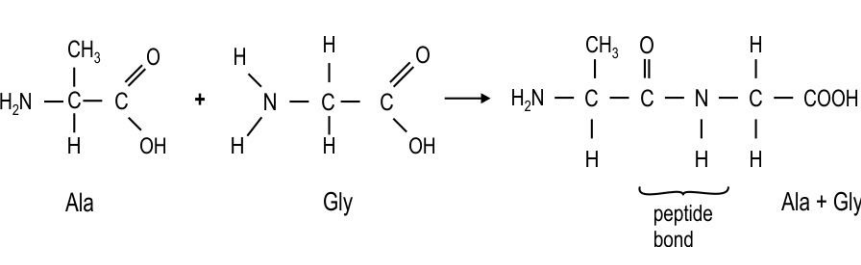
Which of the following statements is/are true for the above reaction?
(i) A dipeptide Gly-Ala is equally likely to be formed by condensation of alanine and glycine.
(ii) Water is eliminated in the above condensation reaction.
(iii) Oxygen and hydrogen is released as gases in the above condensation reaction.
Assertion (A): The denaturation of proteins can destroy all and protein structures.
Reason (R): Curdling of milk is due to denaturation of proteins.
The correct option among the following is
Which of the following molecules is eliminated during peptide bond formation?
Name the chemical bonds found in protein, fat, water and polysaccharide.
What is the condition for basic nature of amino acid?
What is the condition for acidic nature of amino acid?