Preparation of Carboxylic Acids and its Derivatives
Preparation of Carboxylic Acids and its Derivatives: Overview
This topic consists of concepts such as Preparation of Carboxylic Acids by Oxidation of Primary Alcohols and Aldehydes, Preparation of Carboxylic Acids by Oxidation of Alkylbenzenes, Preparation of Carboxylic Acids by Hydrolysis of Nitriles and Amides in Acidic Medium, Preparation of Carboxylic Acids by Reaction of Grignard Reagent with Carbon Dioxide, etc.
Important Questions on Preparation of Carboxylic Acids and its Derivatives
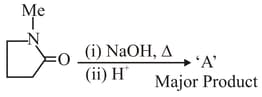 is
is
Glyceraldehyde
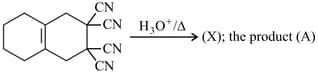
The products formed in the above reaction are
The major product '' formed in the given reaction is
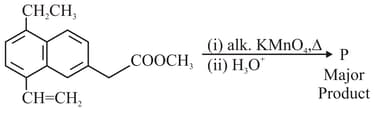
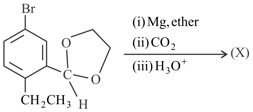
The number of - bonds in is , then the value of is _____ .
What is the major product of the following reaction?
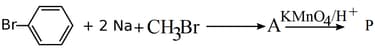
(P is the major product in the reaction)
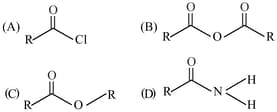
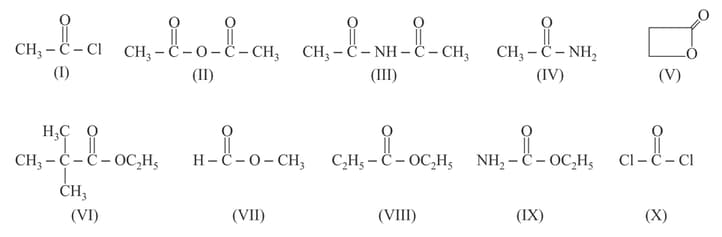
The correct order of their reactivity towards hydrolysis at room temperature is :
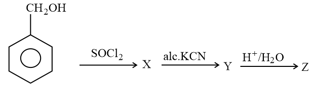
Degree of unsaturation in compound is
When ethyl butanoate undergo reaction with and then out of ethyl and butyl group which forms acid and why?
Examine the structural formulas shown below, and find out how many compounds will show the oxidation reaction with acidic .
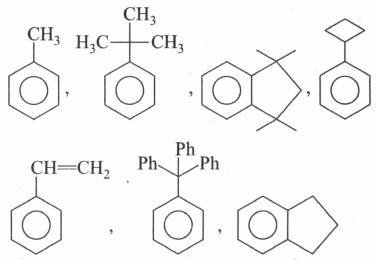
How many compounds out of the following are more reactive than ethyl acetate towards hydrolysis?
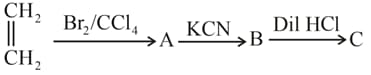
In the above reaction sequence, the product is
The compound in the following reaction scheme:
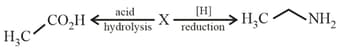 is:
is:
Which one of the following functional groups undergoes hydrolysis with alkali to yield an acid group?
The final product in the reaction is :
How will you convert bromoethane into ethanoic acid ?
Alkyl halides are converted into nitriles by the action of aqueous or aqueous-alcoholic . The reaction follows mechanism and works best with primary and secondary alkyl halides. Aryl halides are extremely less reactive towards nucleophilic substitutions. Identify the correct procedure for the following conversion.
-Chloroethanol into -hydroxypropanoic acid.
Alkyl halides are converted into nitriles by the action of aqueous or aqueous-alcoholic . The reaction follows mechanism and works best with primary and secondary alkyl halides. Aryl halides are extremely less reactive towards nucleophilic substitutions. Identify the correct procedure for the following conversion.
tert-butyl bromide into -Dimethylpropanoic acid.
Alkyl halides are converted into nitriles by the action of aqueous or aqueous-alcoholic . The reaction follows mechanism and works best with primary and secondary alkyl halides. Aryl halides are extremely less reactive towards nucleophilic substitution. Identify the correct procedure for the following conversion.
-Chlorobutane into -Methylbutanoic acid
Alkyl halide are converted into nitriles by the action of aqueous or aqueous-alcoholic . The reaction follows mechanism and works best with primary and secondary alkyl halides. Aryl halides are extremely less reactive towards nucleophilic substitutions. Identify the correct procedure for the following conversion.
-Nitrochlorobenzene into -Nitrobenzoic acid