Optical Isomerism
Optical Isomerism: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as D- and L- Configuration, Nicol Prism and Plane Polarised Light, Dextrorotatory and Laevorotatory, Optical Isomers or Enantiomers and Optical Isomerism, Asymmetric Carbon or Stereocenter, Racemic Mixture, etc.
Important Questions on Optical Isomerism
When an optically active compound is placed in a 10 dm tube, it is present 20 gm in a 200 mL solution rotates the PPL by 30o. Calculate the angle of rotation and specific angle of rotation if above solution diluted to 1 litre.
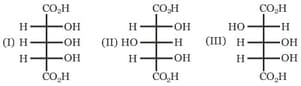
Which of the following combinations amongst the four Fischer projections represents the same absolute configurations?
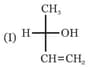
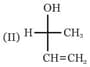
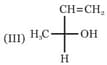
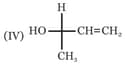
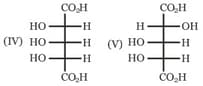
Which of the above formula represent identical compounds?
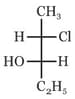
The compound with the above configuration is called:
Which of the following sugars has the configuration (2S, 3R, 4R)?
Dextrorotatorypinene has a specific rotation . A sample of pinene containing both the enantiomers was found to have a specific rotation value . The percentages of the (+) and (-) enantiomers present in the sample are, respectively.
Dextrorotatorypinene has a specific rotation . A sample of pinene containing both the enantiomers was found to have a specific rotation value . The percentages of the (+) and (-) enantiomers present in the sample are, respectively.
What kind of reagent would be needed to resolve a racemic amine, such as 2-aminobutane?
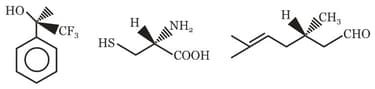
The R/S configuration of these compounds are respectively.
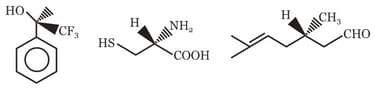
The R/S configuration of these compounds are respectively.
A pure simple of -chlorobutane shows rotation of PPL by in standard conditions. When above samples is made impure by mixing its opposite form, so that the composition of the mixture become -form and -form, then what will be the observed rotation for the mixture.
The optically active tartaric acid is named as tartaric acid because it has a positive
One enantiomer in solution rotates the plane of polarised light to the right, whereas the other rotates it to the left.
A solution containing equal concentrations of two enantiomers does not rotate the plane of polarised light (the two opposing effects cancel each other out) and is known as a
Explain the properties of Enantiomers?
Define resolution of racemic mixture.
For a laevorotatory compound a negative () sign is placed before the degree of rotation.
A compound that rotates the plane polarised light in the anticlockwise direction, is said to be laevorotatory.
Differentiate between dextrorotatory and laevorotatory compounds.
Define a laevorotatory compound.
