General Introduction of Hydrocarbons
General Introduction of Hydrocarbons: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Alkenes, Isomerism in Alkenes, Ring Chain Isomerism in Alkyne & Functional Group Isomerism in Alkyne etc.
Important Questions on General Introduction of Hydrocarbons
C1 - C2 bond is shortest in:
Geometrical isomers can be
The compound 1, 2-butadiene has:
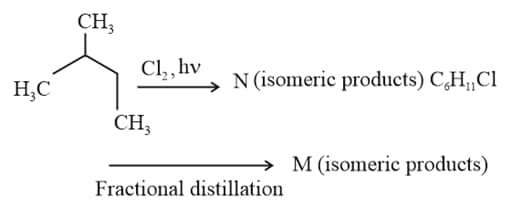
The compound which has one isopropyl group, is –
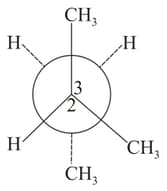
is rotated bond. The resulting conformer is
The stable conformer of ethane is
Isomers which can be interconverted through rotation around a single bond are
contains X number of allylic hydrogen and contains Y number of allylic hydrogen.The number of structural isomers of are
Which of the following is functional group isomer of 2-butene?
butene and butene exhibit which type of isomerism among the following?
Give the chain isomers of the compound with the molecular formula .
Explain chain isomerism in alkenes with examples.
Alkenes are weakly polar just like alkanes.
The bond angle between two hybrid orbitals of carbon atoms in _____ is .
The alkenes are soluble in _____.(non-polar solvents/polar solvents)
What is the bond angle between hybrid orbitals of carbon atoms in alkenes?
The bond angle between two hybrid orbitals of carbon atoms in alkenes is
Describe sawhorse projections of alkanes.
Draw Sawhorse projections for the eclipsed and staggered conformations of ethane. Which of these conformations is more stable and why?