Particle Nature of Electromagnetic Radiation
Particle Nature of Electromagnetic Radiation: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Black Body Radiation, Properties of Black Body, Particle Nature of Electromagnetic Radiations & Evidences of Particle Nature of Electromagnetic Radiations etc.
Important Questions on Particle Nature of Electromagnetic Radiation
The energies of two radiations are and , respectively. The relation between their wavelength i.e., will be:
The energy absorbed by each molecule of a substance is and bond energy per molecule is What will be the kinetic energy of the molecule per atom?
The energy of second Bohr orbit of the hydrogen atom is hence the energy of fourth Bohr orbit would be :
The value of Planck’s constant is The velocity of light is Which value is closest to the wavelength in meters of a quantum of light with frequency of
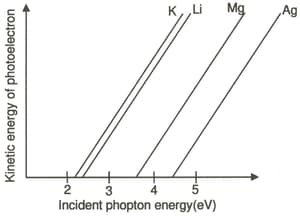
The photoelectric behaviour of and metals is shown in the plot below. If light of wavelength is incident on each of these metals, which of them will emit photoelectrons? [Planck's contant ; velocity of light ]
Name the phenomenon which shows the quantum nature of electromagnetic radiation.
The frequency of radiation emitted, when an electron falls from to in a Hydrogen atom would be
(Given, ionisation energy of Hydrogen is and
If the maximum kinetic energy of photoelectrons ejected from a metal surface when it is irradiated with a radiation of frequency is then the threshold frequency of the metal is _______
The kinetic energy of the photoelectrons ejected from a metal on irradiation with light of frequency is K. When irradiated with light of frequency , the kinetic energy of the photoelectrons becomes . What is the threshold frequency of the metal?
In case of photoelectric effect, slope of vs curve is (where - stopping potential, subjected frequency)
Photoelectric effect shows:
Energy of an electron is given by . Calculate the wavelength of light required to excite an electron in a hydrogen atom from will be
Select the correct statement about the photoelectric experiment from the following.
The energy difference between the ground state of an atom and its excited state is , calculate the wavelength of the photon required to induce the transition.
Light of wavelength , shines on a metal surface with intensity , and the metal emits electrons per second of average energy . What will happen to and if is doubled?
The "Kangri" is an earthen pot used to stay warm in Kashmir during the winter months. Assume that the "Kangri" is spherical and of surface area It contains of a mixture of coal, wood and leaves with calorific value of (and provides heat with efficiency). The surface temperature of the 'Kangri' is and the room temperature is Then, a reasonable estimate for the duration t (in hours) that the 'kangri' heat will last is (take the 'kangri' to be a black body):
A zinc ball of radius, charged to a potential The ball is illuminated by a monochromatic ultraviolet light with a wavelength The photoelectric threshold for zinc is The potential of ball after a prolonged exposure to the is
A certain metal has a work function of . It is irradiated first with of light and later with of light. Among the following, the correct statement is: [Given:Planck constant Speed of light ]
Ultra-violet light is shone on a zinc surface and photoelectrons are emitted. The graph shows how the stopping potential varies with frequency
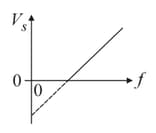
Planck's constant may be determined from the charge of an electron multiplied by
A certain stellar body has radius and temperature and is at a distance of from the earth. Here, refers to the earth-sun distance and and refer to the sun's radius and temperature, respectively. Take, both star and sun to be ideal black bodies. The ratio of the power received on earth from the stellar body as compared to that received from the sun is close to
