Ionic Equilibrium in Solution
Ionic Equilibrium in Solution: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Electrolytes, Strong Electrolytes, Weak Electrolytes, Non-electrolytes, Ionic Equilibrium & Degree of Dissociation for Acids and Bases etc.
Important Questions on Ionic Equilibrium in Solution
undergoes dissociation as if . dissociation of is " ", report your answer as
What is the concentration in of a solution of glucose which is isotonic with a deci-normal solution which is dissociated?
The electrochemical equivalent of a material depends on
Sodium chloride conducts electric current in its solid state.
In which of the following solution should the other electrode be immersed to get maximum e.m.f , If galvanic cell is composed of two hydrogen electrodes, one of which is a standard one.
( for acetic acid and for phosphoric acid .
A certain weak acid has a dissociation constant of . What is the value of the equilibrium constant for its reaction with a strong base?
At equilibria, select the false statement, considering the given equation:
and have equal value of dissociation constants as at . The equilibrium constant for the reaction of and will be:
The relation between the degree of dissociation of a weak electrolyte and van't Hoff factor is expressed by the expression:
The ionisation constant of $\mathrm{NH}_{4}^{+}$ in water is $5.6 \times 10^{-10} \mathrm{at}$ $25^{\circ} \mathrm{C} .$ The rate constant for the reaction of $\mathrm{NH}_{4}^{+}$ and $\mathrm{OH}^{-}$ to form $\mathrm{NH}_{3}$ and $\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}$ at $25^{\circ} \mathrm{C}$ is $3.4 \times 10^{10}$ litre
$\mathrm{mol}^{-1} \mathrm{sec}^{-1} .$ If equilibrium constant of water at $25^{\circ} \mathrm{C}$ is $1.8 \times 10^{-16},$ then
The degree of dissociation of $\mathrm{NH}_{4} \mathrm{OH}$ is :
At infinite dilution, the percentage ionisation of both strong and weak electrolytes is:
Acetic acid and propionic acid have values and respectively at a certain temperature. An equimolar solution of a mixture of the two acids is partially neutralized by . How is the ratio of the contents of acetate and propionate ions related to the values and the molarity ?
The solubility product of is What is the concentration of ions in that solution?
Which of the following salts will not undergo hydrolysis?
The solubility of a solute in water varies with the temperature as follows: .
For which of the following solute, plot is:
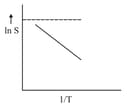
when represents the enthalpy of the solution?
Aniline behaves as a weak base.When 0.1M, 50ml solution of aniline was mixed with 0.1M, 25ml solution of HCl the pH of resulting solution was 8. Then the pH of 0.01 M solution of aniliniumchloride will be (Kw = 10-14)
Electrolytes when dissolved in water dissociates into ions because
An acid solution of 0.005 M has a pH of 5. The degree of ionisation of acid is
Vapour density of at is found to be . The degree of dissociation of is:
