Integrated Rate Equations of Chemical Reaction
Integrated Rate Equations of Chemical Reaction: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Integrated Rate Equation for Zero Order Reactions, Half Life Period for Zero Order Reactions, Kinetics of Reversible Reactions & Reversible First Order Reactions etc.
Important Questions on Integrated Rate Equations of Chemical Reaction
A first order reaction is complete in minute. Calculate the time taken for the reaction to be complete:
,
The half life of a radioactive isotope is three hours. If the initial mass of the isotope were 256 g, the mass of it remaining undecayed after 18 hours would be
In a first-order reaction, the concentration of reactant decreases from in. The rate constant of reaction in is
The reaction is found to be zero order reaction. If it takes seconds for an initial concentration of to go from , what is the rate constant for the reaction.
The rate constant for a first order reaction is . Calculate its life time.
For a parallel first order reaction is:
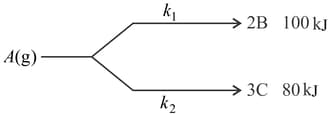
If reaction starts with pure , then at any stage of reaction, mole of in product is . Then activation energy for overall reaction is:
If an optically active compound 'A' decompose through given parallel 1st order kinetics.
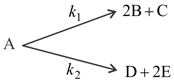
Initial mole of is . If only & are optically active compounds and their angle of rotation per mole are respectively, then which of the following is/are correct -
The kinetic data for the given reaction is provided in the following table for three experiments at .
| Ex No. | [Initial rate ( sec )] | ||
In another experiment starting with initial concentration of and respectively for and at . Find the rate of reaction after 50 minutes from start of experiment (in )?
Consider a reaction . If initial concentration of is then select correct graph.
For a zero-order reaction, with the initial reactant concentration , the time for completion of the reaction is:
The rate of the haemoglobin -carbon monoxide reaction,
has been studied at . The Concentration of reactants are expressed in
| Rate of disappearance of | ||
The rate constant for the reaction is . The value of is
The reaction was found to be second order in . The rate constant for the reaction was determined to be . If the initial concentration is what is the value of in sec?
(Express your answer by multiplying with 100 and rounding off to two significant figures)
For the reaction: It is found that a plot of Versus time is linear, and that in , the decreases from to , If the rate constant is in , report the value of A by rounding it off to one decimal and multiplying with 2.
What is the half-life for the decomposition of when Given that for
(Express you answer up to one significant figures and in multiple of )
A substance decomposes according to second order rate law. If the rate constant is mole Calculate half-life of the substance, if the initial concentration is .
If the value of half life is , Report the value of
Catalytic decomposition of nitrous oxide by gold at at an initial pressure of was in minutes and in minutes. Find the order of the reaction and report the value of how much percentage will it decompose in minutes at the same temperature, but at an initial pressure of
The decomposition of arsine in to arsenic and hydrogen is a first order reaction. The decomposition was studied at constant volume and at constant temperature. The pressures at different times are as follows:
If the velocity constant (in ) value is A h-1, Report the answer by multiplying A with 100 and rounding off to the nearest integer value.
The gas-phase decomposition of is of second order in with at The initial concentration of in the flask at In how many seconds does it take up of this
\
Give answer after rounding off to the nearest integer value.
Which of the following is incorrect?
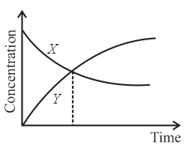
The accompanying figure depicts the change in concentration of species and for the elementary reaction as a function of time. The point of intersection of two curves represents:
