Integrated Rate Equations of Chemical Reaction
Integrated Rate Equations of Chemical Reaction: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as Integrated Rate Equation for Zero Order Reactions, Half Life Period for Zero Order Reactions, Time-Concentration Graph for Zero Order Reactions, Integrated Rate Equation for First Order Reactions, etc.
Important Questions on Integrated Rate Equations of Chemical Reaction
A first order reaction is complete in minute. Calculate the time taken for the reaction to be complete:
,
In a first-order reaction, the concentration of reactant decreases from in. The rate constant of reaction in is
Acid catalysed hydrolysis of esters is pseudo first order reactions because water is present in excess in given reaction.
For acid catalysed hydrolysis of ester rate law obtained is rate , where . What is the half-life if the initial concentrations are for the ester and for the catalysing acid?
Select the correct statement for a first-order reaction from the following.
The hydrolysis of ester is a
The half life of a first order reaction is . Fraction of the reactant left behind after from the beginning is
Graph of half life of first-order reaction and initial concentration of reactant is a:
Graph of half life of zero-order reaction and initial concentration of reactant is a:
The consecutive reaction takes place in a closed container. Initially, the container has moles of (and no and ). The plot of total moles of the constituents in the container as a function of time will be
Which among the following represents the expression for life of order reaction?
If the rate constant of a first order reaction is , then find the time required for of the reactant to reduce to .
If the decomposition reaction follows first order kinetics, then the graph of rate of formation of denoted by against time will be
If the rate constant for a first order reaction is then find the time required for completion of of the reaction.
Reactant gives different products in parallel first order reactions. Rate constant for the formation of any produet is where For the decay of what is the overall rate constant in terms of
For a zero-order reaction, with the initial reactant concentration , the time for completion of the reaction is:
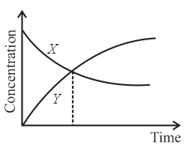
The accompanying figure depicts the change in concentration of species and for the elementary reaction as a function of time. The point of intersection of two curves represents:
The order of a reaction for which a linear line (with a negative slope) is obtained in a graph of vs is:
Two-third life for a first-order reaction is minutes. The value of its velocity constant is nearly
For a first order reaction , the rate constant is . If the initial concentration of is , the concentration of at any time is given by the expression:
