Kinetics of Some Complex Reactions
Kinetics of Some Complex Reactions: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as Reversible First Order Reactions, Integrated Rate Expression for Second Order Reactions with Two Reactants, Kinetics of Successive Reactions, Half-life Expression of nth Order Reaction, etc.
Important Questions on Kinetics of Some Complex Reactions
For a parallel first order reaction is:
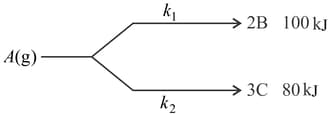
If reaction starts with pure , then at any stage of reaction, mole of in product is . Then activation energy for overall reaction is:
A substance undergoes first order decomposition involving two parallel first order reactions as :
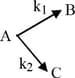
The mole percentage of in the products is approximately :
For a hypothetical elementary following reaction,
 Where
Where
initially, only moles of are present. Find the total no. of moles of and at the end of reaction.
A compound dissociates by two parallel reactions through the first-order path at a fixed temperature:
In a closed vessel, the reaction is started with pure , with of with initial pressure of . What is the pressure (in ) developed in the container after minutes from the start of the experiment?
The concentration of after hours is
The initial rate of consumption of and the sum of the initial rate of formation of and are respectively, taking, equal to
Cotyledons are also called-
Ozone depletion takes place as
Step-1
Step-2
Order of the reaction will be
Bicyclohexane was found to undergo two parallel first order rearrangements. At 730 K, the first order rate constant for the formation of cyclohexane was measured as , and for the formation of methyl cyclopentene, the rate constant was . What is the percentage distribution of the rearrangement products?
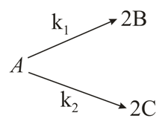
A substance undergoes first order decomposition involving two parallel first order reactions as :
The mole percentage of in the products is approximately :
For a order decomposition of as given
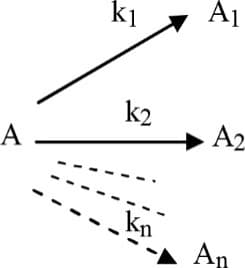
Therefore rate constant for the overall decomposition of is
For reaction , Rate expression is . What of reactant react by mechanism when molar -
If is the initial concentration of the reactant, the half-life period of the reaction of order is proportional to which of the following?
Find out the time required to decompose half of the substance for order reaction is inversely proportional to:
decomposes as:
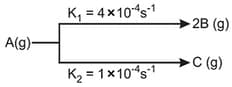
the rate of appearance of , taking concentration of , is equal to:
The forward rate constant for the reversible gaseous reaction is at . What is the rate constant for the backward reaction at this temperature, if moles of and are present in vessel at equilibrium?
Consider the following case of a competing order reaction:
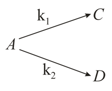
The reaction starts at with only . is equal to at all times. The time in which all three concentrations will be equal is given by:
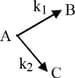
A substance undergoes first order decomposition. The decomposition follows two parallel first order reactions as,
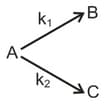
and
Thus the percentage distribution of and are:
The equilibrium between two isomers studies as , Starting with non equilibrium mixture of concentrations molar andmolar. It was found that molar concentration of had reacted at time t (i) Find an expression for reaction Rate
(ii) Find integrated rate equation as where
(iii) Aftercalculate for this reaction.
A follows parallel path I order reactions giving B and C as :
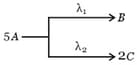
If initial concentration of A is 0.25 M, calculate the concentration of C after 5 hours of reaction.
[Given : ]
