First Law of Thermodynamics
First Law of Thermodynamics: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Sign Conventions for Work, First Law of Thermodynamics, Conclusions from First Law of Thermodynamics & Sign Conventions in Thermodynamics etc.
Important Questions on First Law of Thermodynamics
When mol of a gas is heated at constant volume, temperature is raised from K. If heat supplied to the gas is J, then which statement is correct?
If is the change in enthalpy and the change in internal energy accompanying a gaseous reaction, then
Which among the following are true for an irreversible isothermal expansion of an ideal gas?
A heat engine absorbs heat at temperature and heat at temperature . Work done by the engine is . This data
A gas undergoes change from state to state . In this process, the heat absorbed and work done by the gas is , respectively. Now gas is brought back to by another process during which of heat is evolved. In this reverse process of .
Calculate the internal energy of a gas that absorbs of heat and expands from to against a constant pressure 1 bar.
The ratio Kp to Kc of a reaction is 24.63 L atm mol–1 at 27°C. If heat of reaction at constant pressure is 98.8 kcal, calculate the heat of reaction (in kcal) at constant volume? (Report the value in the nearest integer)
(use values and )
A gas is enclosed in a cylinder with a piston. Weights are added to the piston, giving a total mass of . As a result, the gas is compressed and the weights are lowered . At the same time, of heat is evolved from the system. Calculate the change in internal energy of the system and report the answer in the nearest integer value
For the reaction at ,
Calculate for the reaction at the given temperature.
(Note: Report your answer after multiplying with 100 and rounding up to the nearest integer value.)
The ratio Kp to Kc of a reaction is 24.63 L atm mol–1 at 27°C. If heat of reaction at constant pressure is 98.6 kcal, what is the heat of reaction (in kcal) at constant volume?
The specific heat of a certain substance is . Assuming ideal solution behavior, the energy required (in ) to heat of molal of its aqueous solution from to is closest to :
[Given: molar mass of the substance ; specific heat of water ]
According to IUPAC conventions work done on the surroundings is :
Which of the following statements are correct as per IUPAC sign convention ?
is mathematical expression for
A gas is compressed adiabatically by doing work of . What is the change in internal energy of the gas ?
A system goes from and by two different paths in the diagram as shown in figure. Heat given to the system in path is . Also the work done by the system along path is more than path by . What is the heat exchanged by the system in path ?
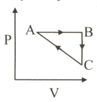
Calculate amount of heat supplied to the gas to go from A to B If internal energy change of gas along AB is 10J. The given figure shows a change of state A to state C by two paths ABC and AC for an ideal gas :
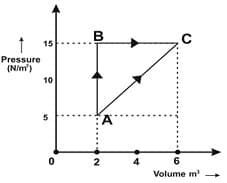
Consider an ideal gas which undergoes a cyclic process as below:
Then the Heat absorbed by the system during process CA is ____
With a change in internal energy, , one mole of a non-ideal gas undergoes a change of state . Then, change in enthalpy of the process in is_______________.
Calculate the increase in internal energy of system when 40 joule heat is supplied and the work done by a system is 8 joule