Nature of heat and work
Nature of heat and work: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as free expansion, work, mechanical work, sign conventions for work and mathematical expression for irreversible work.
Important Questions on Nature of heat and work
Which of the following is the SI unit of work?
Mechanical work is a _____ quantity.
Define mechanical work and give the formula to calculate work. Is work a vector or scalar quantity?
The conditions for a system to be able to completely obtain all the work possible is
Which process has maximum work done?
calorie _____ joule.(write answer up to decimal)
If the work is done by the system, will be negative because _____ .
According to IUPAC conventions work done on the surroundings is :
Which of the following statements are correct as per IUPAC sign convention ?
For next two question please follow the same
The pressure-volume graphs of various thermodynamics processes are shown:
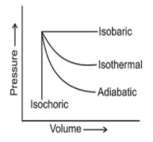
Work is the mode of transference of energy. It has been observed that reversible work done by the system is maximum obtainable work.
wrev > wirr
The works of isothermal and adiabatic processes are different from each other.
If w1, w2, w3 and w4 are magnitude of work done in isothermal, adiabatic, isobaric and isochoric reversible processes, respectively, then the correct sequence (for expansion) would be
The work done during the expansion of a gas from to against a constant external pressure of is
Calculate the work done in each of the following reactions. State whether work is done on or by the system.
Decomposition of of at
Calculate the work done in each of the following reactions. State whether work is done on or by the system.
The oxidation of one mole of at .
of nitrogen is expanded isothermally and reversibly at from when the work done is found to be. Find the final pressure.
Three moles of an ideal gas are compressed isothermally and reversibly to a volume of . The work done is at . Calculate the initial volume of the gas.
Calculate the maximum work when of oxygen are expanded isothermally and reversibly from a pressure of to at.
One mole of an ideal gas is compressed from against a constant pressure of . The work involved in the process is. Calculate the final volume.
Three moles of an ideal gas are expanded isothermally from a volume of to at against a pressure of . Calculate the work done in and joules.
In what reaction of the following, work is done by the system on the surroundings?
