Spontaneous Processes (Irreversible Process)
Spontaneous Processes (Irreversible Process): Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Spontaneity, Spontaneous Reactions, Non-spontaneous Reactions, Spontaneous Processes in Nature, Driving Force for Spontaneity and, Spontaneity in Terms of Entropy Change
Important Questions on Spontaneous Processes (Irreversible Process)
The correct relationship between free energy and equilibrium constant K of a reaction is:
Consider the following reaction occurring in automobile
the sign of would be:
Match list-I (Equations) with List-II (Type of processes) and select the correct option.
| List I | List II | ||
| Equations | Type of processes | ||
| (1) | Kp > Q | (i) | Non spontaneous |
| (2) | (ii) | Equilibrium | |
| (3) | Kp = Q | (iii) | Spontaneous and endothermic |
| (4) | (iv) | Spontaneous |
For vaporization of water at 1 atmospheric pressure, the values of respectively. The temperature when Gibbs energy change for this transformation will be zero, is:
The values of for the reaction, respectively. This reaction will be spontaneous at
A chemical reaction will be spontaneous if it is accompanied by a decrease of
Identify the correct statement for change of Gibb’s energy for a system at constant temperature and pressure:
The enthalpy and entropy change for the reaction
are respectively. The temperature at which the reaction will be in equilibrium is
Which of the following pairs of a chemical reaction is certain to result in a spontaneous reaction?
Considering entropy (S) as a thermodynamic parameter, the criterion for the spontaneity of any process is:
Standard enthalpy and standard entropy changes for the oxidation of ammonia at are respectively. The standard Gibbs energy change for the same reaction at is:
Unit of entropy is:
The Nernst equation for the reaction, , in terms of the free energy change is:
The equilibrium concentrations of the species in the reaction are respectively at . for the reaction is
Consider the graph of Gibbs free energy G vs extent of reaction. The number of statement/s from the following which are true with respect to points (a), (b) and (c) is
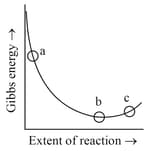
A. Reaction is spontaneous at (a) and (b)
B. Reaction is at equilibrium at point (b) and non-spontaneous at point (c)
C. Reaction is spontaneous at (a) and non-spontaneous at (c)
D. Reaction is non-spontaneous at (a) and (b)
The entropy and enthalpy changes for the process . At what temperature this reaction occurs spontaneously?
The spontaneity means, having the potential to proceed without the assistance of external agency. The process which occurs spontaneously are:
Standard enthalpy and standard entropy changes in a certain process at are and respectively. Standard gibbs energy change of this process is:
The molar entropies of at are respectively. Using the given below, The bond energy of is . Find out the value of .
Calculate the temperature above which the reduction of lead oxide to lead in the following reaction becomes spontaneous.
