Law of Chemical Equilibrium and Equilibrium Constants
Law of Chemical Equilibrium and Equilibrium Constants: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Law of Mass Action, Forward Rate Constant, Backward Rate Constant, Equilibrium Constant, Active Mass, Equilibrium Law or Law of Chemical Equilibrium & Equilibrium Equation etc.
Important Questions on Law of Chemical Equilibrium and Equilibrium Constants
An expression for the backward rate constant of the reaction, is
The reaction is elementary order reaction opposed by elementary secondary order reaction. When started with equimolar amounts of and at equilibrium, it is found that the concentration of is twice that of Specific rate constant for forward reaction is The specific rate constant for backward reaction is
For the reaction,
What is when the equilibrium concentration of and ?
The reaction
is in equilibrium in a closed vessel at The partial pressure (in atm) of in the reaction vessel is closest to:
[Given: The change in Gibbs energies of formation at and bar for
Gas constant ]
Find the number of reaction which will be favoured in backward direction:
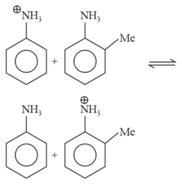
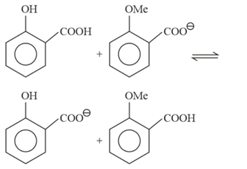
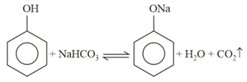
Find the approximate value of for the given equilibrium reaction, when moles of and mole of are allowed to react in a container of capacity and the following equilibrium is established:
, given that the equilibrium mixture requires of acidified solution.
When the two reactants and are mixed to give products and , the reaction quotient at the initial stage of the reaction
For the given reaction at equilibrium, at .
at this temperature is . Find value of (Round off n up to the one decimal place)
For the following equilibrium, at .
Both the forward and reverse reactions in the equilibrium are elementary bimolecular reactions. What is for the reverse reaction in terms of . Find value of n.
Enter your answer from these options :
Equilibrium constant for reaction is . Hence equilibrium constant for ionization .The value of is:
For the following gaseous equilibrium,
is found to be equal to . This is attained when the temperature is:
For the reaction, A(s) + 2B(g) 2C(g) + D() at TK
Find the value of Kp when the equilibrium contains 25% of B(g) by volume of the gaseous species.
For the reaction,
What is when the equilibrium concentration of and ?
The decay profiles of three radioactive species and are given below:
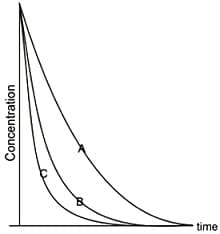
These profiles imply that the decay constants and follow the order
The concentrations of the reactant A in the reaction at different times are given below
| Concentration (M) | Time (Minutes) |
| 0.069 | 0 |
| 0.052 | 17 |
| 0.035 | 34 |
| 0.018 | 51 |
The rate constant of the reaction according to the correct order of reaction is:
Nine volumes of a gaseous mixture consisting of gaseous organic compound A and just sufficient amount of oxygen required for complete combustion yielded on burning four volumes of , six volumes of water vapour and two volumes of , all volumes measured at the same temperature and pressure. If the compound contains C, H and N only, the molecular formula of the compound A is:
In a chemical reaction, the rate constant for the backward reaction is 7.5 × 10–4 and the equilibrium constant is 1.5. The rate constant for the forward reaction is -
The rate constant at for the reaction of & to form is & ionisation constant of is . The rate constant of proton transfer to is -
In a chemical reaction, the rate constant for the backward reaction is and the equilibrium constant is . The rate constant for the forward reaction is -
In reversible reaction , rate constant of forward reaction is & rate constant of backward reaction is . Equilibrium constant is -
