Thermodynamics of Equilibrium
Thermodynamics of Equilibrium: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Relationship between Equilibrium Constant (K) & Reaction Quotient (Q) and Gibbs Free Energy Change (ΔG) etc.
Important Questions on Thermodynamics of Equilibrium
The Haber’s process for the formation of at is . Which of the following is the correct statement?
The enthalpy and entropy change for the reaction
are respectively. The temperature at which the reaction will be in equilibrium is
In a one-litre flask, moles of undergoes the reaction . The progress of product formation at two temperatures (in Kelvin), and , is shown in the figure:
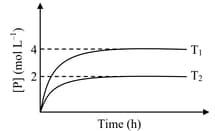
If and , then the value of is
[ and are standard Gibb's free energy change for the reaction at temperatures and , respectively.]
What is the (approx) partial pressure of at equilibrium at ?
Which of the following is correct at equilibrium?
Select the graph which can be used to determine standard free energy of the reaction given below:
Assume that the reaction is at equilibrium.
Among the following set of conditions, which condition necessarily holds true for a non-feasible process?
(Where, equilibrium constant)
Calculate the temperature given that the value of and of are and the reactants and is in equilibrium with .
The value of for the following reaction at is:
Given, standard Gibbs energy change at the given temperature is
For the following reaction,
the . What is the value of of the reaction at ?
Consider that for a hypothetical reaction, and are and at What is the equilibrium constant for the reaction at
Consider the curve between and . Which plot will be correct for exothermic reaction?
Among the following, select the correct option if there is an increase of pressure on system at a constant temperature.
The plot of against is a straight line with a positive slope ( being the equilibrium constant of a reaction). The correct statement among the following is:
What is the value of free energy change for a reversible reaction at equilibrium?
Only a few reactions are simple or straight forward, $i . e .$ purely first, second or third order reactions. But in most of the reactions, the interpretation of variety of data becomes difficult due to several other reactions taking place simultaneously along with the main reaction and thus smooth progress of the reaction is disturbed. Such reactions include the following different types. The reactions, in which a substance reacts or decomposes in more than one way, are called parallel or competing or side reaction. The reactions which take place exclusively on the walls of containing vessels are known as surface reactions. The reactions in which the products of chemical change react together to form the original reactants are called reversible reactions or opposing reactions or counter reactions. The reactions which proceeds from reactants to final products through one or more intermediate stages are called consecutive reactions.
The relation is valid for:
The ionisation constant of in water is at . The rate constant for the reaction of and to form and at is . If dissociation constant of water at is . If of water at is then the heat of neutralisation is:
The change in standard Gibbs energy for a reaction at equilibrium, $eg . \mathrm{PCl}_{5}(g) \rightleftharpoons \mathrm{PCl}_{3}(g)+\mathrm{Cl}_{2}(g),$ on addition of an inert gas at constant pressure and then at constant volume respectively are :
moles of taken in a one litre flask dissociates to extent to reach equilibrium. What is of the reaction ?
Solid is heated in a closed container to When equilibrium is reached, the pressure becomesSimilarly, the equilibrium pressure at was found to be . Hence for the given reaction.
At this temperature range is:
