Raoult's Law
Raoult's Law: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as Raoult's Law, Raoult's Law for an Ideal Solution of Two Liquid Components, Raoult's Law for a Solution Containing a Non-Volatile Solute in a Liquid, Variation of Vapour Pressure of a Mixture with Composition, etc.
Important Questions on Raoult's Law
Under what condition Henry's law becomes special case of Raoult's Law?
Two liquids are mixed together to form a mixture which boils at same temperature and their boiling point is higher than the boiling point of either of them, so they show _____ from Raoult's law.
The vapour pressure of the solution is affected by adding the _____ solute.
When will the vapour pressure of the volatile liquid lowered?
The vapour pressure of water is at . Now, calculate the vapour pressure of molar solution of a solute in it.
A mixture of toluene and benzene forms a nearly ideal solution. Assume and to be the vapor pressures of pure benzene and toluene, respectively. The slope of the line obtained by plotting the total vapor pressure to the mole fraction of benzene is:
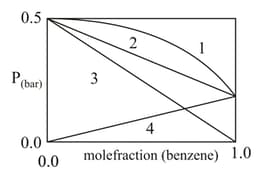
In the pressure vs. the mole fraction of benzene curves/lines shown below, the total vapour pressure of an ideal mixture of benzene and toluene will follow the curve/line.
Vapour pressure of benzene is . When of non-volatile solute is dissolved in benzene, benzene solution has vapour pressure . Calculate the molar mass of the solute in ( molar mass of benzene = ).
Raoult's law states that for a solution of volatile liquids, the partial vapour pressure of each component of the solution is directly proportional to its mole fraction present in solution.
_____ law which states that for a solution of volatile liquids, the partial vapour pressure of each component of the solution is directly proportional to its mole fraction present in solution.
The following is a graph plotted between the vapour pressure of two volatile liquids against their respective mole fractions.
Which of the following statement is correct ?
For a dilute solution containing of a non-volatile non-electrolyte solution in of water, the elevation in boiling point at pressure is Assuming the concentration of solute is much lower than the concentration of the solvent, the vapor pressure of the solution is ()
Which of the following units is most useful in relating concentration of solution with its vapour pressure?
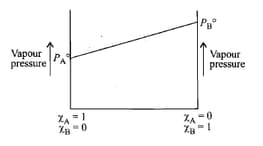
When partial pressure of solvent in solution of non-volatile solute is plotted against its mole fraction, nature of graph is
Partial pressure of solvent (mole fraction) in solution of non-volatile solute (mole fraction) is given by equation,
Explain the determination of molar mass of a solute from relative lowering in vapour pressure.
In an equilibrium at with a benzene-toluene solution, the mole fraction of benzene is 0.400, then, what is the mole fraction of toluene in vapour phase?
Mark the correct statement(s) from the following.
Select the correct option from the following colligative effect:
