Relative Lowering of Vapor Pressure
Relative Lowering of Vapor Pressure: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Colligative Properties, Relative Lowering of Vapour Pressure, Factors Affecting Colligative Properties & Ostwald and Wacker's Experiment etc.
Important Questions on Relative Lowering of Vapor Pressure
Which among the following is a colligative property?
The mass of a non-volatile, non-electrolyte solute (molar mass ) needed to be dissolved in 114 g octane to reduce its vapour pressure by 75 %, is:
A solution contains of urea per litre of water. Another solution contains of cane sugar per litre of water at the same temperature. What is the ratio of lowering of vapour pressure in solutions of and ?
What is the vapour pressure of a solution containing of water and of sucrose at ?
Give your answer by rounding off to the nearest integer value.Molecular weight of sucrose is .
The pressure of the water vapour of a solution containing a non-volatile solute is below that of the vapour of pure water. Determine the molality of the solution.
Round off your answer to nearest integer value.
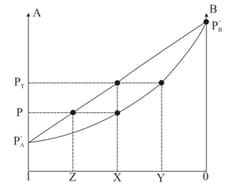
Mole fraction of liquid in liquid solution.
Mole fraction of vapour in vapour mixture.
is the graphical mid point between .
Find value of . [Given ]
If of
of
Give your answer after multiplying with 10 and round off to the nearest integer.
Two beaker are placed in a sealed flask. Beaker A initially contained 0.15 mol of naphthalene (non-volatile) in 117 g of benzene and beaker B initially contained 31 g of an unknown compound (non-volatile, non-electrolytic) in 117 g of benzene. At equilibrium, beaker A is found to have lost 7.8 g of weight. Assume ideal behaviour of both solutions to answer the following question.
The molar mass of solute in solution B is closest to:
Relative lowering of vapour pressure is a colligative property because _____.
Colligative properties depend on _____.
Relative vapour pressure lowering depends only on.
Vapour pressure of solution of a non volatile solute is always
Lowering of the vapour pressure of the solution:
A solution of methanol and ethanol has a vapour pressure of at , where is the mole fraction of methanol. Hence,
Identify the inappropriate statement.
Find the value of mole fraction of the solute when vapour pressure of glucose is at in dilute solution.
Consider the following statements.
(i) On adding Methyl alcohol to water, boiling point of water increases.
(ii) When is added to water, depression in freezing point is observed.
(iii) Diffusion of solvent occurs from a region of its higher concentration to a region of its lower concentration.
Identify the correct options.
Find the correct relation between of acids HA1 and HA2 (assuming they are taken in same concentration), if lowering of vapour pressure $\Delta \mathrm{P}_{1}$ of an aqueous solution of acid HA1 and $\Delta \mathrm{P}_{2}$ of an aqueous solution of acid HA2, are related as .
Among the following aqueous solutions, which has a lowest boiling point?
An ideal solution of two pure liquids and are having the vapour pressure of and respectively at the temperature . The liquid solution of and is made up of of each and . Then, find the pressure when of mixture has been vaporised.
