Solubility
Solubility: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Solubility of a Solid in a Liquid, Effect of Dielectric Constant of a Solvent on Solubility of a Solid in a Liquid & Effect of Lattice Energy and Solvation Energy on Solubility of a Solid in a Liquid etc.
Important Questions on Solubility
The molar solubility (in ) of a sparingly soluble salt is ‘s’. The corresponding solubility product is ‘s’ is given in terms of by the relation :
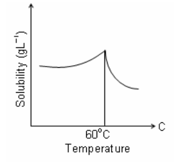
Solubility curve of a hydrated salt in water with temperature is given. The curve indicates that the solution process is
The Henry law constant for in water at respectively. Calculate , of solution made by dissolving air at 1 bar pressure. [Given:
and have large dielectric constant but the not a good solvent why?
Given liquid solution contains two components and . Component follows Henry's law for the mole fraction range at constant temperature (and low pressure, where, it can be taken ) . Then component must follow Raoult's law for the molefraction range . What is the value of ?
Explain the solubility of ionic compounds in polar solvents.
Give two examples each of polar and non-polar solvents.
, a toxic gas with a rotten egg-like smell is used for the qualitative analysis. If the solubility of in water at is , Calculate Henry's law constant. (Write the answer without units)
Henry’s law states that at a constant temperature, the solubility of a gas in a liquid is inversely proportional to the partial pressure of the gas present above the surface of liquid or solution.
Henry's Law states that amount of gas that is dissolved in a liquid is directly proportional to the _____ pressure of that gas above the liquid when the temperature is kept constant.
The values of the Henry's law constant of and in water at are and , respectively. The order of their solubility in water at the same temperature and pressure is
What is the concentration of dissolved oxygen at under pressure of one atmosphere if partial pressure of oxygen at is .
(Henry’s law constant for oxygen)
Which of the following is correct match for separation?
Is the nature of solute important when preparing a solution of a specified concentration?
Which of the following factors affect the solubility of a gaseous solute in the fixed volume of liquid solvent?
[A] Nature of solute [B] Temperature [C] Pressure
What are the examples of miscible and immiscible liquids ?
