Gas Laws and Ideal Gas Equation
Gas Laws and Ideal Gas Equation: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as Density and Molar Mass Relation, Gas Laws, Boyle's Law, Isotherm in Graph, Isobar in Graph, Isochore in Graph, Payload Capacity of Hot Air Balloon, and Vapour Density.
Important Questions on Gas Laws and Ideal Gas Equation
A bubble of air is underwater at temperature and the pressure 1.5 bar. If the bubble rises to the surface where the temperature is and the pressure is 1.0 bar, what will happen to the volume of the bubble?
The correct value of the gas constant is close to:
If are pressure, volume, molar mass, temperature and gas constant respectively, then for an ideal gas, the density is given by
What is the value of at STP for of hydrogen gas?
The volume of gas along with the solid substance is pressure and pressure. What is the volume of the solid substance ?
The density of the gaseous mixture in a vessel at 2.1 atmosphere and 310 K is 1.35 g/litre. If a small pin-hole is made on the wall of the vessel, through which gases effuse, then which of the following is the correct composition of the gases He and effusing out initially?
From a certain apparatus, the diffusion rate of hydrogen has an average value of . The diffusion of another gas under the same conditions is measured to have an average rate of . Identify the gas.
What should be the percentage increase in pressure for a decrease in volume of a gas at constant temperature?
A gas is heated from to at pressure. If the initial volume of the gas is , its final volume would be
Air expands on heating and hence its density _____. (increases/ decreases)
For a fixed amount of gas at constant temperature, volume of a gas is _____ proportional to the pressure of a gas.
Two separate bulbs contain ideal gas and . The density of gas is twice that of . The molecular mass of is half that of . The two gases are at the same temperature. The ratio of pressure to that of gas is:
The slope for an isochore plotted for a van der Waal's gas neglecting molecular attractions is equal to:
In Charles' law, the line of the volume vs temperature graph is known as
According to the Boyle's law, as the pressure increases volume
Boyle's law equation : p =_____.
Give its mathematical form of Boyle's law.
State and explain Boyle's law.
Write important characteristics of a gas based upon kinetic theory of gases.
Match the following columns :
Columns-I Columns-II
(Graphical representation) (X and Y coordinates)
(i) 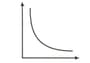 (a) pV vs V
(a) pV vs V
(ii) 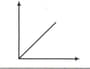 (b) p vs V
(b) p vs V
(iii) 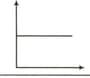 (c) p vs 1/V
(c) p vs 1/V
