Liquefaction of Gases and Critical Constants
Liquefaction of Gases and Critical Constants: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Liquefaction of Gases, Andrew's Isotherms, Expression of Critical Volume & Inversion Temperature etc.
Important Questions on Liquefaction of Gases and Critical Constants
An ideal gas can’t be liquefied because
Which gas among the following is the easiest to liquify?
The critical temperature of is less than because the molecules have:
The expression of in terms of and is:
From Andrew's Isotherm experiment can be calculated.
For which compound Andrew Thomson performed his experiment.
The critical volume of a gas when expressed in terms of Van der Waals constants and takes the form:
The van der Waals constant 'a' for different gases are given below:
| Gas | () |
The gas that can be most easily liquefied is
Which one of the following gases has the highest critical temperature?
If helium is allowed to expand in vacuum, it liberates heat because.
What is the correct increasing order of liquefiability of the gases shown as in the graph below?
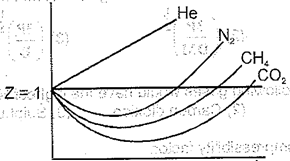
The most favourable conditions to liquefy a gas are:-
For a real gas, the curve was experimentally plotted, and it had the following appearance. With respect to liquefaction. Choose the correct statement.
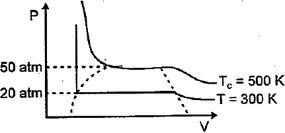
If for the gases, the critical temperature mentioned below i.e.:
| Gas | Critical temp. |
Which of the following can be predicted?
An ideal gas can't be liquefied because :
Select the correct order followed by boyle's temperature , critical temperature and inversion temperature .
The temperature above which a gas cannot be liquefied by applying pressure is known as:
What will be the value of (critical volume) ?
The correct order regarding magnitude of critical temperature , Boyle's temperature and inversion temperature for any particular gas is
What should be the volume occupied by grams of oxygen gas () at and , provided:
(Given: )
