Adsorption
Adsorption: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as Adsorbent, Adsorbate, Adsorption of Gases on Solids, Mechanism of Adsorption, Desorption, Degree of Adsorption, Enthalpy of Adsorption, Entropy of Adsorption, Gibbs Free Energy of Adsorption, etc.
Important Questions on Adsorption
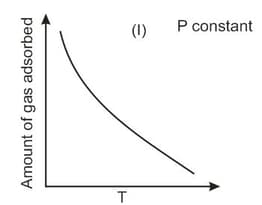
The given graphs/data I, II, III and IV represent general trends observed for different physisorption and chemisorption processes under mild conditions of temperature and pressure. Which of the following choice(s) about I, II, III and IV is (are) correct?
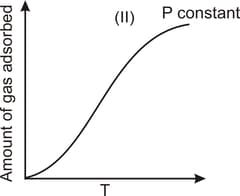
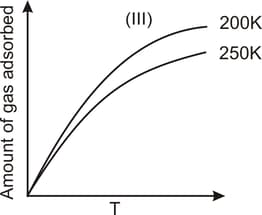
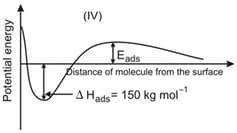
Among physisorption and chemisorption, which type of a adsorption has a higher enthalpy of adsorption?
20% of surface sites are occupied by molecules. The density of surface sites is and total surface area is . The catalyst is heated to 300 K while is completely desorbed into a pressure of 0.001 atm and volume of . The number of active sites occupied by each molecule will be
Adsorption of gases on solid surface is generally exothermic because:
Describe briefly about Adsorption isostere.
What is the effect of surface area on chemical adsorption.
How is physical adsorption affected by surface area?
How long animal charcoal retains its absorbent properties?
What is the difference between charcoal and activated charcoal?
Is chemisorption irreversible or endothermic?
Which adsorption is irreversible adsorption?
Explain the active centre catalyst adsorbs reactants which result in a greater rate of reaction?
Why chemical adsorption high specific in nature ?
The colouring matter removed by animal charcoal during purification of sugar acts as an: