Enthalpy Change of a Reaction- Reaction Enthalpy
Enthalpy Change of a Reaction- Reaction Enthalpy: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as Enthalpy of Reaction, Standard Enthalpy of Reactions, Enthalpy of Formation, Standard Enthalpy of Formation, Enthalpy Change during Phase Transformations, Enthalpy of Fusion, Enthalpy of Vaporization, etc.
Important Questions on Enthalpy Change of a Reaction- Reaction Enthalpy
Enthalpy change for the reaction,
The dissociation energy of bond is:
From the data of following bond energies:
Calculate the enthalpy of the following reaction in .
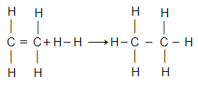
Given that bond energies of respectively and for , bond enthalpy of is:
For which one of the following equations is equal to for the product?
Bond dissociation enthalpy of respectively. The enthalpy of formation of HCl is:
Assume each reaction is carried out in an open container. For which reaction will
For the reaction:
at constant temperature, is:
Standard heat of formation of , and are: and , respectively. Then, the average value of bond energy in is
Calculate (in joules) for from the following data,
Enthalpy of vaporisation can be defined as the enthalpy change that accompanies the vaporisation of ten moles of liquid at any temperature and pressure.
Nitroglycerine detonates according to the following equations,
The standard molar enthalpies of formation, for all the compounds are given below.
The enthalpy change when of nitroglycerine is detonated is
From the following data
The standard enthalpy of formation of in is
Write a thermochemical equation to depict standard enthalpy of sublimation ?
Standard enthalpy of _____ is the change in enthalpy when one mole of a solid substance sublimes at a constant temperature and under standard pressure.
A container holds moles of gas and moles of gas in it at a constant pressure of . The gases are separated by a wall and the whole container is held in an ice bath at a constant temperature of . The wall is removed and the gases mix and react to form by the reaction given below. After the reaction comes to equilibrium how many grams of the ice have melted ? Consider that all heat produced in reaction has been utilized in melting of ice.
| Compound | ||
|---|---|---|
| A | ||
| B | ||
| C |
All data above is at . .
Read the passage and answer the following questions as single choice correct .
Mass of ice melted in the reaction may be
Given that
The enthalpy of formation of carbon monoxide will be
Which of the following reaction defines ?
In the reaction : kcal and kcal,
heat of formation of is
Given the following equations and values at ,
.
.
.
Calculate for the following reaction, .
Given the following equations and values at ,
.
.
.
Calculatefor the following reaction,
