Internal Energy
Internal Energy: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Internal Energy, Characteristics of Internal Energy, Thermodynamical Interpretation of Ideal Gas, Change in Internal Energy for Ideal Gas & Law of Equipartition of Energy etc.
Important Questions on Internal Energy
Internal energy and pressure of a gas per unit volume are related as:
A container is filled with moles of an ideal diatomic gas at absolute temperature When heat is supplied to gas temperature remains constant but moles dissociates into atoms. Heat energy supplied to gas is?
Which amongst the following options is the correct relation between change in enthalpy and change in internal energy?
of heat is given to one mole of oxygen at keeping the volume constant. Raise in temperature is
According to law of equipartition of energy, the average energy associated with each degree of freedom is:
A thermally insulated rigid container of volume contains a diatomic ideal gas at room temperature. A small paddle installed inside the container is rotated from the outside, such that the pressure rises by . The change in internal energy is close to
The internal energy of an ideal gas is plotted against volume for a cyclic process , as shown in the figure.
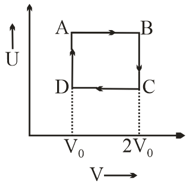
The temperature of the gas at and are and , respectively. The heat absorbed by the gas (in ) in this cyclic process, is :
How much heat will be required at constant volume at to form of from and
Given:
one mole of an ideal gas at is expanded isothermally from an initial volume of to . The for this process is:
An ideal gas initially at temperature with expands adiabatically into vacuum to double its volume. The final temperature is given by:
A diatomic ideal gas changes its state from to as shown in the figure.
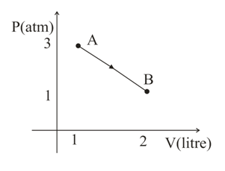
Choose the correct versus graph: (where is internal energy of the gas)
Which of the following statement is INCORRECT ?
The internal energy of an ideal gas increases during an isothermal process when the gas is :-
of heat is provided to the system. Work done on the system is . What is the change in internal energy?
One mole of an ideal gas at is expanded isothermally from an initial volume of to . The for this process is ( )
In the reaction, if moles of react with moles of , then is equal to
A gas does of work on its surroundings and absorbs of heat from the surroundings. Hence, is
When a sample of an ideal gas is allowed to expand at constant temperature against an atmospheric pressure,
To break one bond in DNA, the amount of energy to be supplied is 0.06 eV. The value of this energy in joules is approximately;
