Le-chatelier's Principle
Important Questions on Le-chatelier's Principle
Consider the following reaction, .
In the above reaction, find out whether you have to increase (or) decrease the volume to increase the yield of the product.Consider the following reaction, .
In the above reaction, find out whether you have to increase (or) decrease the volume to increase the yield of the product.Consider the following reactions, .
In the above reaction, find out whether you have to increase (or) decrease the volume to increase the yield of the product.
Deduce the Van't Hoff equation.
The partial pressure of carbon dioxide in the reaction is at . Calculate at for the reaction. for the reaction is and does not change in the given range of temperature.
The equilibrium constant for the reaction is at and at . Calculate for the reaction.
What is the effect of added inert gas on the reaction at equilibrium?
State Le-Chatelier's principle.
For the reaction, . The following molecular scenes represent different reaction mixture (A – green, B – blue)
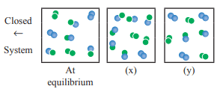
What is the effect of increase in pressure for the mixture at equilibrium?
In the above reaction at equilibrium, the reaction mixture is blue in colour at room temperature. On cooling this mixture, it becomes pink in colour. On the basis of this information, which one of the following is true?
Solubility of carbon dioxide gas in cold water can be increased by
The formation of ammonia from and is a reversible reaction, .
What is the effect of increase of temperature on this equilibrium reaction?

