Specific Heat Capacity
Specific Heat Capacity: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as Heat, Heat Capacity, Specific Heat Capacity & Molar Specific Heat Capacity etc.
Important Questions on Specific Heat Capacity
If the heat given to raise the temperature of two solid spheres of radius and and density and through is same, then the ratio of their specific heat capacity is:
An electric fan and a heater are marked as 100 W, 220 V and 1000 W, 220 V respectively. The resistance of heater is
Match the column
Column - 1 Column - 11
(A) Specific heat capacity (P) depends on mass
(B) Latent heat (Q) Property of substance alone
(C) Heat capacity (R) Independent of mass
(D) Water equivalent (S) Property of object alone
The water flowing from the H tap fills the empty container in 3t by itself, the water flowing from the C tap in 2t. Temp of H-tap is 80°C and that of C-tap is 40°. Both taps are opened simultaneously. What is the final temp of water of the filled container?
(Heat exchange is only between waters.)
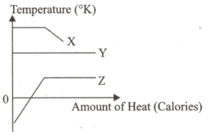
Temperature change graphs due to temperature
increase of X, Y and Z items are given in the
figure.
So w~ich of the X, Y and Z graphs could be
correct?
The graph of the temperature values shown by
X and Y thermometers in an environment are as
shown in the figure.
Accordingly, when the 30 ° X value is measured
in X thermometer, how many O Y does Y
thermometer show?
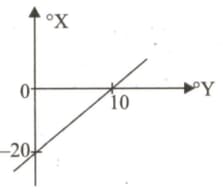
An X thermometer shows the freezing
temperature of water at sea level as -15 °X and
the boiling temperature as 125 °X.
What temperature Celcius thermometer will
show if X thermometer reads 13 ?
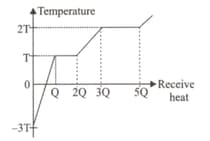
A solid material is heated by a heater that gives
equal heat at equal intervals. Study the graph
of Temp-Heat supplied to the solid object given
below
Which of following statements are correct?
I. Melting heat is smaller than the evaporation
temperature.
II. Boiling temperature is 2T.
III. Its Specific heat for solid is less than its
liquid specific heat.
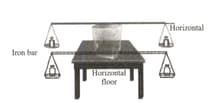
It is observed that when a very thin iron rod
with weights placed on its pan is placed on the
upper surface of the ice mass, whose vertical
section is show the diagram, the rod descends
by melting the ice, and the places where the rod
passes become ice again.
Which of following statements are correct?
I. If the weights on the pans are increased, the
wire reaches the ground faster.
II. The higher the pressure, the lower the
melting point of the ice.
III. If the thickness of the wire is increased, the
wire reaches the ground faster.
Two liquids with different initial temperatures
are placed in identical heat-insulated containers
and heated by identical heaters. The final
temperatures of the fluids heated for an equal
time become equal.
Accordingly, the liquids, can have same value
of
I. Mass, II. Specific heat,
III. Heat capacity
If the specific heat of a substance is infinite, it implies
Two bodies are in thermal equilibrium if they have the same
ice at is mixed with of water at . The final temperature is
When the temperature is gradually decreased, the specific heat of a substance is
Two liquids have densities in the ratio of and specific heat in the ratio of . The ratio of the thermal capacity of an equal volume of those liquids is
How much ice must be added to water at in order to reduce its temperature to ?
The amount of heat required to convert of ice (specific ) at - to steam at is
of ice at and of water at are mixed. The temperature of the mixture will be
A beaker contains 40 g of water a . Now of ice is put into the beaker. The resulting temperature will be
When the temperature of water rises, the rate of evaporation.