Collisions
Collisions: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as Collisions, Linear Momentum and Collisions, Perfectly Inelastic Collision in Oblique Direction & Collision of a Ball with a Wall etc.
Important Questions on Collisions
For head-on collision between two colliding balls of equal radii , the impact parameter is equal to
A ball is dropped from height . After striking the ground time it rebounds to height . Then coefficient of restitution is
A ball is dropped from height above floor. Ball continuously bounces on the floor. Find speed just after second bounce if coefficient of restitution is :-
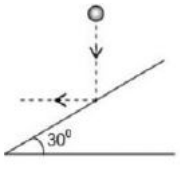
A ball is released from a point, it goes vertically downwards and collides with a fixed smooth inclined plane of angle of inclination of . After the collision the ball goes horizontally. The coefficient of restitution between the ball and the inclined plane is
In perfectly inelastic collisions, the relative velocity of the bodies
In an inelastic collision involving an isolated system, the final total momentum is _____.
Which of the following is not conserved in an inelastic collision.
Which of the following collisions cannot be oblique, according to the definition of oblique collision?
What is the ratio of the final to initial relative speed between two objects after they collide known as:
The law of conservation of momentum states that the sum of momenta of two bodies before collision is equal to the sum of momenta after collision provided that
Two bodies of different masses m, and m, have equal momenta. Their kinetic energies E, and E, are in the ratio?
Which one of the following is true for an elastic collision between two bodies?
A heavy truck moving with a velocity of collides with a light drum at rest. If the collision be elastic, then velocity of drum immediately after the collision will be
A bullet is fired from a rifle and the rifle recoils. Kinetic energy of rifle is
In elastic collision, energy transfer takes place when
If the collision between the block and the incline is completely elastic, then the vertical (upward) component of the velocity of the block at point immediately aafter it strike the second incline is
Two objects of the same mass and with the same initial speed, moving in a horizontal plane, collide and move away together at half their initial speeds after the collision. The angle between the initial velocities of the objects is,
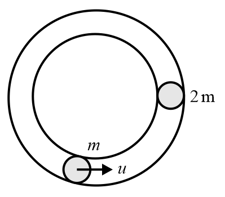
Two masses and are placed in a fixed horizontal circular smooth hollow tube as shown. The mass is moving with speed and the mass is stationary. After their first collision, the time elapsed for next collision is (Coefficient of restitution is, )
In perfectly inelastic collisions, the relative velocity of the bodies:
A metal ball falls from a height of on to a steel plate and jumps up to a height of . The coefficient of restitution of the ball and steel plate is
