Variation of Traits - Environmental factors also affect expression of traits, and hence affect the probability of occurrences of traits in a population. Thus the variation and distribution of traits observed depends on both genetic and environmental factors.
Variation of Traits - Environmental factors also affect expression of traits, and hence affect the probability of occurrences of traits in a population. Thus the variation and distribution of traits observed depends on both genetic and environmental factors.: Overview
This topic covers various concepts like Cell Division, Characteristics of Garden Pea Plants, etc.
Important Questions on Variation of Traits - Environmental factors also affect expression of traits, and hence affect the probability of occurrences of traits in a population. Thus the variation and distribution of traits observed depends on both genetic and environmental factors.
If R and r alleles are for shape of seed in pea plant and the frequency of recessive allele is 30%. Then how much seed should have round shape out of 1000 seeds?
In maize, the trait for the purple kernel (P) is dominant over the yellow kernel (p). A plant with purple kernels is crossed with another plant with yellow kernels and produces 2 offspring with purple kernels and 2 offspring with yellow kernels. Identify the genotypic and phenotypic ratios obtained from the cross in (b).
In maize, the trait for the purple kernel (P) is dominant over the yellow kernel (p). A plant with purple kernels is crossed with another plant with yellow kernels and produces 2 offspring with purple kernels and 2 offspring with yellow kernels. What is the genotype of the parental maize plants?
What is the formula for genotype calculation?
Which of the following character was not a part of Mendel's experiments?
The following characters are observed in different pea plants :
A) Seeds round, flowers white, flowers in axial position.
B) Pods inflated, seeds wrinkled, pods green.
C) Seeds green, pods constricted, flowers violet.
D) Flowers white, pods yellow, flower position terminal.
How many characters are dominant and recessive in each plant mentioned above according to the studies of G.J. Mendel respectively?
The correct answer is :
Which one of the following genotypes can form only 2 different types of gametes?
Differentiate between traits and alleles
Although plant cell has no centrosomes, but how do their cell division happen?
In Mendelian dihybrid cross, how many of progeny in generation possess genotype rryy?
In Mendelian dihybrid cross, how many individuals are heterozygous of both the character in -generation?
In Mendelian dihybrid cross, how many individuals are homozygous recessive for one of the character only in generation?
In Mendelian dihybrid cross, how many individuals are homozygous dominant for both the genes in generation?
Which is correct about traits chosen by Mendel?
A term alternative forms of a gene is called _____.
Define alleles of a gene?
Mendel's experiment on sweet pea plants with yellow round seeds (YYRR) and green wrinkled seeds (yyrr). Explain with in detail with the help of the schematic diagram given below.
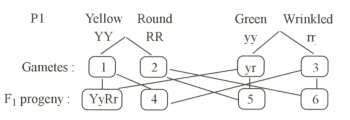
Name the phenotypes produced in F2 progeny upon self-pollination of F1 progeny.
Mendel's experiment on sweet pea plants with yellow round seeds (YYRR) and green wrinkled seeds (yyrr). Explain it in detail and give the F2 progeny ratio.
Repeated use of antibiotics can develop resistance.
Define the term allele.
