Conditional Probability and Multiplication Theorem
Conditional Probability and Multiplication Theorem: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as Conditional Probability, Properties of Conditional Probability, and Multiplication Rule of Probability.
Important Questions on Conditional Probability and Multiplication Theorem
A signal which can be green or red with probability and respectively, is received by station A and then transmitted to station B. The probability of each station receiving the signal correctly is If the signal received at station B is green, then the probability that the original signal was green is:
If are two events, such that , then find .
Jake and Elisa are given a mathematics problem. The probability that Jake can solve it is . If Jake has solved it, the probability that Elisa can solve it is . Otherwise, the probability that Elisa can solve it is . Draw a tree diagram to illustrate the above question, showing clearly the probabilities on each branch. Find the probability that at least one of the students can solve the problem.
Jake and Elisa are given a mathematics problem. The probability that Jake can solve it is . If Jake has solved it, the probability that Elisa can solve it is . Otherwise, the probability that Elisa can solve it is . Draw a tree diagram to illustrate the above question, showing clearly the probabilities on each branch. Find the probability that Jake solves the problem, given than Elisa has.
Jake and Elisa are given a mathematics problem. The probability that Jake can solve it is . If Jake has solved it, the probability that Elisa can solve it is . Otherwise, the probability that Elisa can solve it is . Draw a tree diagram to illustrate the above question, showing clearly the probabilities on each branch.
The Venn diagram illustrates the number of students taking each of the three sciences: physics, chemistry and biology.
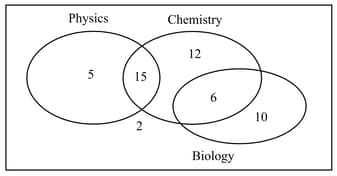
A student is randomly chosen from the group.
Find the probability that the student studies physics, given that they study chemistry. (Write answer in simplest fraction form)
. Find the probability with technology.
Two fair tetrahedral dice with faces numbered and are thrown. The discrete random variable is defined as the product of the two numbers thrown. Find .
A group of investors own properties in north European cities. The following Venn diagram shows how many investors own properties in Amsterdam, Brussels or Cologne. One of the investors is chosen at random.

You are given that and . Calculate the remaining regions shown in the Venn Diagram.
A supermarket uses two suppliers, and of strawberries. Supplier supplies of the supermarkets's strawberries. Strawberries are examined in a quality control inspection (): of the strawberries supplied by pass and of the strawberries from pass .
A strawberry is selected at random.
Given that the strawberry passes , find the probability that it came from supplier .
(Round off and Write answer up to decimal places)
A group of investors own properties in north European cities. The following Venn diagram shows how many investors own properties in Amsterdam, Brussels or Cologne. One of the investors is chosen at random.

Find (Round off and write up to decimal places )
A group of investors own properties in north European cities. The following Venn diagram shows how many investors own properties in Amsterdam, Brussels or Cologne. One of the investors is chosen at random.
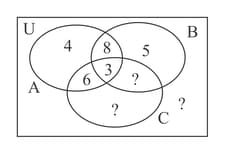
Find (Round off and write up to decimal places)
The probability distribution of a discrete random variable is defined by this table:
Find .
(Write answer in fraction form).
If find .
If and , then find .
If and then find
The letters of the word "" are arranged at random. The probability that arrangements starts with vowel and end with consonant is
A man is known to speak the truth out of times. If he throws a die and reports that it is six, then the probability that it is actually five is
When two dice are rolled, let be the probability of getting a sum of the numbers appear on the dice is at most . Let be the probability of getting a sum at least once when a pair of dice are rolled times. In order to have the minimum is
A coin is tossed three times, where event : head on third toss, event : heads on first two tosses. Determine .
