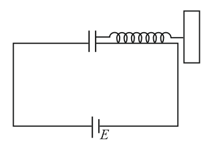
Force between Plates of a Capacitor
Force between Plates of a Capacitor: Overview
This topic covers the concept of Force between Plates of a Charged Parallel Plate Capacitor.
Important Questions on Force between Plates of a Capacitor
A dielectric slab is inserted between the plates of an isolated capacitor. The force between the plates will
If an electron enters into a space between the plates of a parallel plate capacitor at an angle with the plates and leaves at an angle to the plates. The ratio of its kinetic energy while entering the capacitor to that while leaving will be
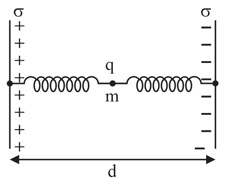
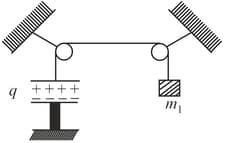
Two large non conducting plates having surface charge densities respectively, are fixed d distance apart. A small test charge q of mass m is attached to two non conducting springs each of spring constant k as shown in the figure. The sum of lengths of both springs in undeformed state is . The charge is released from rest with both the springs nondeformed. Then charge will (neglect gravity)
A parallel plate capacitor has an electric field of between the plates. If the charge on the capacitor plate is , the force on each capacitor plate is:
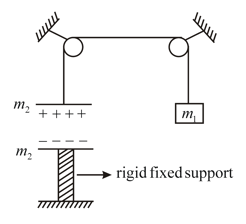
In the given figure a capacitor of plate area is charged up to charge . The mass of each plate is . The lower plate is rigidly fixed. Find the value of so that the system remains in equilibrium -
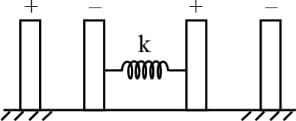
Two charged capacitor have their outer plates fixed and inner plates connected by a spring of force constant . The charge on each capacitor is . Find the extension in the spring at equilibrium-
In the given system a capacitor of plate area is charged up to charge . The mass of each plate is . The lower plate is rigidly fixed. Find the value of so that the system is in equilibrium -
A parallel plate capacitor having charge on it and plate area , has separation between the plates. If one of the plates is pulled to make the final separation , then work done in this process is:
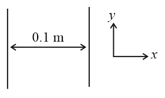
Two insulating plates are both uniformly charged in such a way that the potential difference between them is . (,, plate is at a higher potential). The plates are separated by and can be treated as infinitely large. An electron is released from rest on the inner surface of plate . What is its speed when it hits plate 2? (=1.6
A capacitor is connected to a battery. When separation between them is halved, the force of attraction between the plates
One plate of a capacitor is connected to a spring as shown in the igure. Area of both the plates is . In steady-state, the separation between the plates is (spring was unstretched and the distance between the plates was when the capacitor was uncharged). The force constant of the spring is