Cells in Series and in Parallel
Cells in Series and in Parallel: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as Series Grouping of Cells and Parallel Grouping of Cells.
Important Questions on Cells in Series and in Parallel
Two cells of emf and and internal resistance and , are connected in parallel with each other. Obtain expressions for the equivalent emf and equivalent internal resistance of this parallel combination.
Two cells having the internal resistance and are connected in parallel. The voltage across the battery terminals is . The emf of first cell is , the emf of second cell is (in volt) . Write the value of where is the greatest integer function.
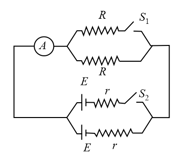
In the circuit shown in figure, reading of ammeter will:
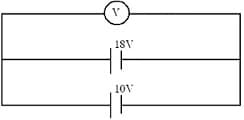
A battery of the emf and internal resistance of and another battery of emf and internal resistance of are connected as shown in figure. Then the voltmeter reading is
Assertion: When cells are connected in parallel to the external load, the effective e.m.f increases.
Reason: Because the effective internal resistance of the cells decreases.
Assertion: When cells are connected in parallel to the external load, the effective e.m.f. increases.
Reason: All the cells will be sending the current to the external load in the same direction.
Assertion: When cells are connected in series to the external load the effective e.m.f. increases.
Reason: The cells help each other in sending the current to the external load.
Assertion: When cells are connected in parallel to the external load, the effective e.m.f increases.
Reason: Because the effective internal resistance of the cells decreases.
Assertion: When cells are connected in parallel to the external load, the effective e.m.f. increases.
Reason: All the cells will be sending the current to the external load in the same direction.
Assertion: When cells are connected in series to the external load the effective e.m.f. increases.
Reason: The cells help each other in sending the current to the external load.
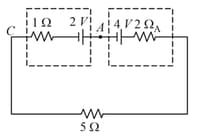
Find the net of the three batteries shown in figure -
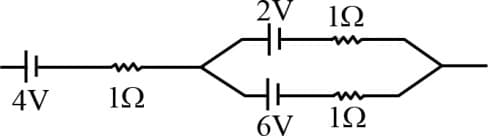
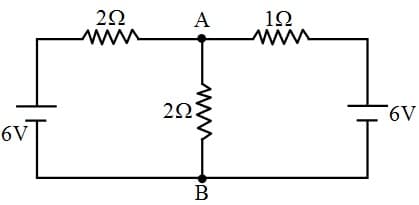
In the diagram shown find the potential at point .
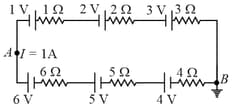
The potential difference between points & in the given diagram is -
Two cells, having the same emf are connected in series through an external resistance . Cells have internal resistances and respectively. When the circuit is closed, the potential difference across the first cell is zero. The value of is -
Which of the following are true, when the cells are connected in series?
identical cells, each of emf and internal resistance , are connected in series to a cell which is joined with reverse polarity. The potential difference across each cell, except , is
Two identical cells send the same current in resistance, whether connected in series or in parallel. The internal resistance on the cell should be,
Twelve cells, each having emf volts are connected in series and kept in a closed box. Some of these cells are wrongly connected with positive and negative terminals reversed. This 12-cell battery is connected with an ammeter, an external resistance and a two-cell battery (two cells of the same type used earlier, connected perfectly in series). The current in the circuit, when the 12-cell battery and 2-cell battery aid each other is when they oppose each other. Then, the number of cells in 12-cell battery that are connected wrongly is,
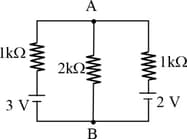
What is the potential drop between points and in the following circuit? Resistances and represent the internal resistance of the respective cells.