Conversion of Galvanometer to Ammeter and Voltmeter
Conversion of Galvanometer to Ammeter and Voltmeter: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Conversion of Galvanometer into an Ammeter, Conversion of an Ammeter to a Higher Range Ammeter, Conversion of Galvanometer into a Voltmeter & Conversion of a Voltmeter to a Higher Range Voltmeter etc.
Important Questions on Conversion of Galvanometer to Ammeter and Voltmeter
A galvanometer has a resistance of . It gives full scale deflection with a current of 2 mA. Calculate the value of the resistance needed to convert it into an ammeter of range
How do you convert a galvanometer into an ammeter?
A current of is required in a galvanometer for full scale deflection. The galvanometer has the coil of resistance . If a maximum current of is to be passed through the galvanometer then the resistance that should be added as shunt is
A galvanometer with its coil resistance requires a current of for its full deflection. In order to construct an ammeter to read up to a current of the approximate value of the shunt resistance should be:
A resistance is connected to a battery of . A galvanometer of resistance is to be used as an ammeter to measure current through the resistance, for this a resistance is connected to the galvanometer. Which of the following connections should be employed if the measured current is within of the current without the ammeter in the circuit?
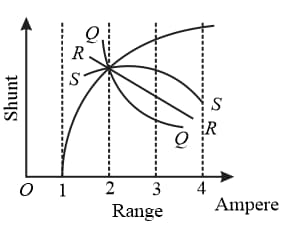
The ammeter has range of , without shunt. The range can be varied by using different shunt resistances. The graph between shunt resistance and range will have the nature as
A moving coil galvanometer of resistance is used as an ammeter using a resistance . The maximum deflection current in the galvanometer is . Find the minimum current in the circuit so that the ammeter shows maximum deflection.
A moving coil galvanometer of resistance is used as an ammeter using a resistance . The maximum deflection current in the galvanometer is . Find the minimum current in the circuit so that the ammeter shows maximum deflection.
A voltmeter has a coil and in series. The coil takes for full-scale deflection. The maximum potential difference which can be measured is -
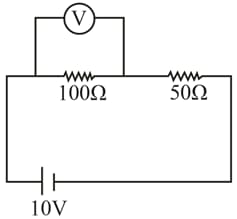
In the given circuit, voltmeter reads The resistance of the voltmeter is:
What resistance should be connected in series of a galvanometer of resistance in order to change its range from volts to volts (in )
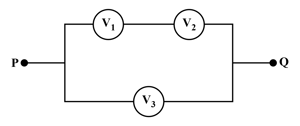
Three voltmeters all having different resistances are joined as shown. When some potential difference is applied across and , their readings are and respectively. Then
The resistance of a voltmeter is . When there is potential difference across its ends, it gives full-scale deflection. What resistance (in ohm) should be connected in series to obtain a full-scale deflection at?
The resistance of an ammeter formed by converting a galvanometer will be:
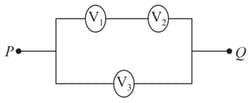
Three voltmeters all having different resistances are joined as shown. When some potential difference is applied across and , their readings are and respectively. Then
The circular coil of a galvanometer has fifty turns. The coil has a radius of . The coil is placed in a radial magnetic field of . The torsion coefficient of the spring on which the coil hangs is . Find the deviation (in degree) of the galvanometer's hand if the current through the coil is .
A voltmeter has a coil and in series. The coil takes for full-scale deflection. The maximum potential difference which can be measured is
A galvanometer is converted to voltmeter by connecting
A galvanometer of resistance requires of the main current as current for full-scale deflection. The value of shunt will be
A moving coil galvanometer, having a resistance produces full scales deflection when a current flows through it. It can be converted into an ammeter of range to by connecting a shunt of resistance to it. If it can also be converted into a voltmeter of range to by connecting a resistance to it in series, then which among the following is correct?
