Electrical Energy and Power
Electrical Energy and Power: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Electric Power, Heat Produced in an Electrical Resistance, Power Transmission, Power Supplied by a Battery, Power Consumed by a Battery & Maximum Power Theorem etc.
Important Questions on Electrical Energy and Power
A potential is applied across a uniform wire of resistance The power dissipation is The wire is then cut into two equal halves and a potential of is applied across the length of each half. The total power dissipation across two wires is The ratio of is The value of is _____.
Different combination of resistors of equal resistance are shown in the figures. The increasing order for power dissipation is:
(A) 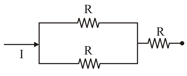
(B) 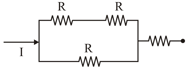
(C) 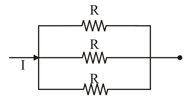
(D) 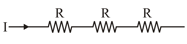
If a wire of resistance is connected across , then power is . The wire is cut into two equal parts and connected with individually, then sum of power dissipated is , then is . Find the value of
In the given circuit when the switch is open, the ammeter reads , two of the four resistances dissipate each and other two resistances dissipate each. If the switch is closed and terminal voltage of the battery is so adjusted that the ammeter reading again becomes , find power dissipation in each of the resistances.
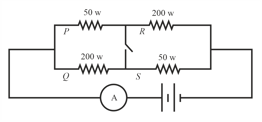
In the given circuit, the value of so that thermal power generated in will be maximum (in ), is:
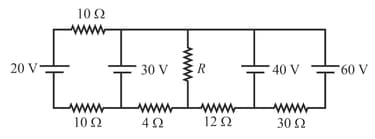
If voltage is applied between terminals and when terminals and are open, the power liberated is and when terminals and are connected, the power liberated is . If the same source is connected to the terminals and , the power liberated in the circuit when terminals and are open is . Determine the power consumed in the circuit when the terminals and are connected and the same voltage is applied between the terminals and .
The internal resistance of the cell shown in figure is negligible. On closing the key , the ammeter reading changes from to , then
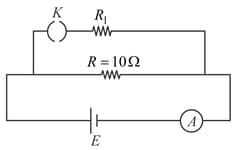
For what value of power across will be ?
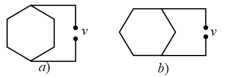
In two - seemingly alike - electric kettles the heating wire is bent into the shape of a regular hexagon. In one of the kettles the heating element was connected as shown in figure a), whilst in the other the heating element was connected as shown in figure b). The ratio of time taken in case a) to case b) is
An electrical bulb rated , is connected in series with another bulb rated , . If the voltage across combination is , the power consumed by the bulb will be about _____ .
Given below are two statements :
Statement I : A uniform wire of resistance is cut into four equal parts. These parts are now connected in parallel. The equivalent resistance of the combination will be .
Statement II : Two resistance and are connected in parallel in an electric circuit. The value of thermal energy developed in and will be in the ratio .
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below
A direct current of and an alternating current of peak value flow through resistance of and respectively. The ratio of heat produced in the two resistances in same interval of time will be :
The charge flowing through a resistor varies with time as . The heat produced in second is about (where is in and is in )
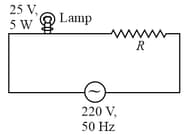
A AC source is connected to a lamp and an additional resistance in series (as shown in figure) to run the lamp at its peak brightness, then the value of (in ohm) will be
A resistor develops of thermal energy in , when a current of is passed through it. If the current increases to , the energy developed in is _____ .
For the circuit show, all wires have negligible resistance, the battery has a constant internal resistance of and the two light bulbs and are identical, each with resistance . The variable resistor is initially set . The switch in the circuit now is closed. To what resistance must the variable resistor be set if bulb is to have the same brightness after the switch is closed as it did with the switch open?
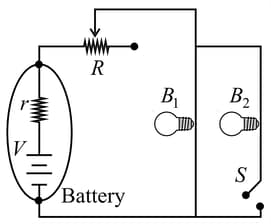
Two bulbs and are given. Which has higher resistance?
In the given circuit, the power generated in resistance will be maximum for equal to,
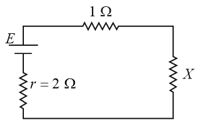
A heater is designed in such a way that it uses when connected to a supply. If the line voltage drops to , the percentage drop in heat output will be
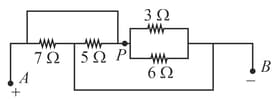
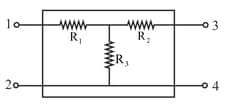
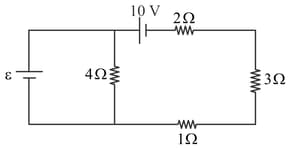
What should be the applied across so that the magnitude of current crossing point becomes of the magnitude of power generated across the largest resistor of the network?