Ohm's Law
Ohm's Law: Overview
In this topic, we will learn that in Ohm’s law the current flowing through a conductor is directly proportional to the potential difference at its ends. The constant of proportionality is called resistance. Variable resistance is used to regulate current without changing voltage.
Important Questions on Ohm's Law
A wire of resistance is gradually stretched to double its original length. It is then cut into two equal parts. These parts are then connected in parallel across a battery. Find the current drawn from the battery.
A voltage of is applied across a carbon resistor with first, second and third rings of blue, black and yellow colours respectively. Calculate the value of current, in , through the resistor.
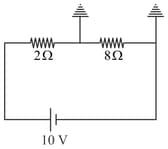
In the circuit shown reading of the ideal voltmeter used is equal to _____ volts.
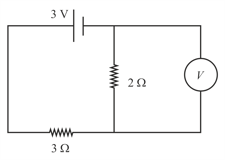
Two cells X and Y are connected to a resistance of as shown in the figure. The terminal voltage of cell Y is
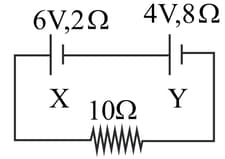
A cell can supply currents of and via resistances of and respectively. The internal resistance of the cell is
In the circuit diagram shown below, and are the potentials at points and respectively. Then. is
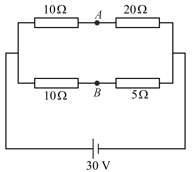
In the electrical network shown in the figure, the potential difference across resistance will be
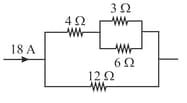
A cylindrical conductor of length and inner radius and outer radius has specific resistance . A cell of emf is connected across the two lateral faces of the conductor. Find the current from the cell.
A wire of length and cross-sectional area has resistance . It carries a current when a voltage is applied to its ends. The wire is melted and drawn to double its length. If the same voltage were to be applied across the wire then
What happens to the resistance if the area of cross section of wire is tripled?
What happens to the resistance of a wire when its length is doubled?
The value of such that the potential difference between and is is
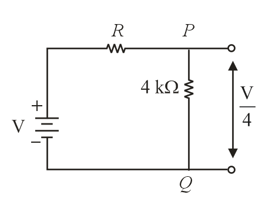
In the circuit shown, the values of the resistances are indicated. The potential difference between the points and is
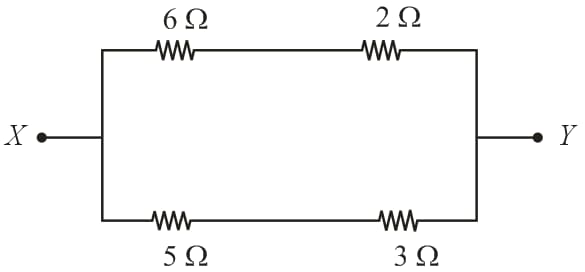
The current passing through the resistance is
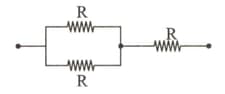
Three equal resistances are connected as shown in the figure. Maximum power that can be dissipated by each resistance is 40 watt. Therefore, the maximum power that can be safety dissipated in the combination is:
The relationship between the current density and the electric field is given by equivalently represents
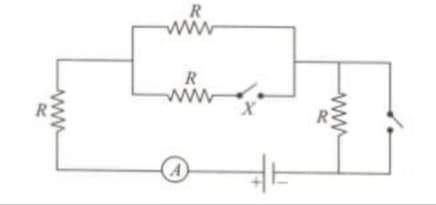
I1 is reading of ammeter if switches X and Y are open and I2 is reading when switches are closed.
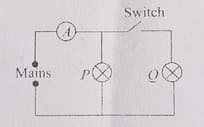
How will the reading in the ammeter A be affected if another identical bulb Q is connected in parallel to P (Fig). The voltage in the mains is maintained at a constant value.
A person connects four 1/4 cells in series but one cell has its terminal reversed. The external resistance is 1 . If each cell has an emf of 1.5V, the current flowing is
In the circuit shown below (on the left) the resistance and the emf source are both variable.
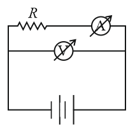
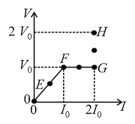
The graph of seven readings of the voltmeter and the ammeter and , respectively) for different settings of resistance and the emf, taken at equal intervals of time , are shown below (on the right) by the dots connected by the curve . Consider the internal resistance of the battery to be negligible and the voltmeter an ammeter to be ideal devices. (Take,
Then, the plot of the resistance as a function of time corresponding to the curve is given by