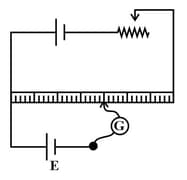
Potentiometer
Potentiometer: Overview
In this topic, we are going to learn about the potentiometer, its structure and its advantages. It also discusses the use of measuring internal resistance with examples.
Important Questions on Potentiometer
Why is a copper wire not used in potentiometer?
How will the position of balance point in the potentiometer will be affected if, (I) current in the potentiometer be increased.
Name the device used for measuring the internal resistance of a secondary cell.
Why is a potentiometer preferred over a voltmeter in measuring the emf of a cell?
What is meant by the sensitivity of a potentiometer? How can it be increased?
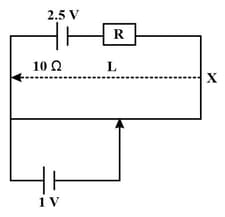
From the potentiometer configuration shown above, the voltage across a battery is found to be . Now a resistor of resistance is added in parallel to the battery. The voltage measured in this case is . Find the internal resistance of the battery.
In a potentiometer arrangement, a cell of emf gives a balance point at length of the wire. If the cell is replaced by another cell and the balance point shifts to , what is the emf of the second cell?
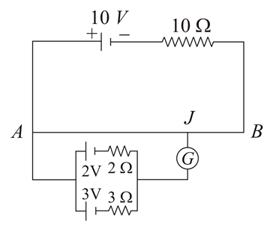
A battery of emf is connected to a uniform wire of length and having a resistance of in series with a resistor as shown in the figure. Two cells of emf and having internal resistances and respectively are connected as shown in the figure. If the galvanometer shows null deflection at point on the wire, the distance of point from the point is __________
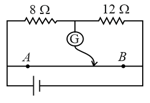
The potentiometer wire shown in figure is long. Where should the free end of the galvanometer be connected on so that the galvanometer may show zero deflection?
A battery of negligible internal resistance is connected across a uniform wire of length. The positive terminal of another battery of emf and internal resistance is joined to the point as shown in figure. Take the potential at to be zero.
(a) What are the potentials at the points and ? (b) At which point of the wire the potential is equal to the potential at ? (c) If the points and are connected by a wire, what will be the current through it? (d) If the battery is replaced by battery, what would be the answers of parts (a) and (b)?
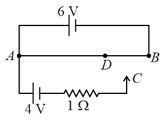
Consider the potentiometer circuit arranged as in figure. The potentiometer wire is long. (a) At what distance from the point should the jockey touch the wire to get zero deflection in the galvanometer? (b) If the jockey touches the wire at a distance of from , what will be the current in the galvanometer?
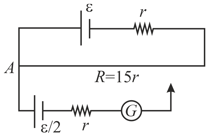
The length of potentiometer wire is . The primary circuit consists of a battery of emf and a resistance of connected in series. In an experiment the balancing length for emf of is obtained at . Find the new balancing if the value of series resistance in the primary circuit is doubled.
Length of a potentiometer wire is . A standard cell of emf is balanced at length of potentiometer wire. How much maximum potential difference can be measured from it?
The resistance of a long potentiometer wire is . An accumulator of emf, negligible internal resistance and a high resistance are connected in series. What is the value of high series resistance, if potential gradient on the potentiometer wire is .
In a potentiometer experiment for the calibration of ammeter, the balanced length of a battery of emf is obtained at . The potential difference across resistance is balanced at of potentiometer wire. If the reading of the ammeter connected in series is , calculate the error in ammeter.
A standard cell of emf is balanced on a length of potentiometer wire. Obtain the balancing length across a resistance , if a current of is flowing through it. Also, calculate the potential gradient.
Potential gradient of potentiometer wire is . In an experiment for calibration of ammeter, potential difference across resistance is balanced across length of potentiometer wire. If the reading of ammeter connected in circuit is . Calculate the error in ammeter reading.
Describe how a potentiometer is used to compare the e.m.f of two cells by (a) direct method (b) combination method.
Explain the principle of potentiometer.
A potentiometer wire has a length of and resistance of . What resistance must be connected in series with the potentiometer wire and a cell of having internal resistance to get a potential drop of along the wire ?