Temperature Dependence of Resistance
Temperature Dependence of Resistance: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Temperature Effect on Resistivity, Resistivity versus Temperature for Conductor, Resistivity versus Temperature for Alloy (Nichrome) & Resistivity versus Temperature for Semiconductor etc.
Important Questions on Temperature Dependence of Resistance
The conductivity of a material varies with temperature for (i) semiconductors and (ii) good conductors as
Given below are two statements: one is labelled as Assertion A and the other is labelled as Reason R.
Assertion A: Alloys such as constantan and manganin are used in making standard resistance coils.
Reason R: Constantan and manganin have very small value of temperature coefficient of resistance.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below.
Resistance of the wire is measured as and at and respectively. Temperature coefficient of resistance of the material of the wire is
The temperature dependence of resistance of and undoped in the temperature range is best described by
The temperature coefficient of resistance of a wire is . At , its resistance is . The resistance of wire will be at
Consider the statements A and B in the previous question. Peltier effect is caused
Previous Question:- Consider the following two statements.(A) Free-electron density is different in different metals.
(B) Free-electron density in a metal depends on temperature. Seebeck effect is caused
A conducting resistance is connected to a battery. The temperature of the conductor decreases due to cooling. The current flowing through the resistance will -
Nichrome or Manganin are widely used in a rheostat because of their,
A piece of Gold (Au) and Germanium (Ge) are cooled from room temperature to 77 K. Then the resistance of
A sliver wire has a resistance of at and a resistance of at Determine the temperature coefficient of resistivity of silver.
The temperature coefficient of resistance of a manganin wire is per degree centigrade and its resistance is at When a potential is applied, its temperature increases to Now what will be its resistance?
Metal alloys are used for making standard resistance coils because
Variation of resistance of the conductor with temperature is as shown. Temperature coefficient of the conductor is
If copper and silicon pieces are heated, the resistance of
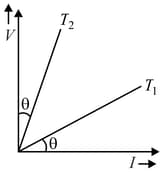
The graphs for a conductor at temperature and are shown in the figure. is proportional to
A wire of Aluminium and a wire of Germanium are cooled to a temperature of . Then
Resistivity of a resistor at a temperature is given by the relation:
Where is the temperature coefficient of resistivity, is resistivity at initial temperature
Assertion: With increase in temperature, resistance of a conducting wire increases.
Reason: With the increase in temperature, the length and area of cross-section of wire changes but resistivity remains constant.
Assertion: The resistivity of semiconductor decreases with increase of temperature.
Reason: In a conducting solid, the rate of collision between free electrons and ions increases with increase of temperature.
Assertion: The temperature dependence of resistance is usually given as, . The resistance of a wire changes from to when its temperature is increased from to . This implies that, .
Reason: is valid only when the change in the temperature, , is small and, .

