Applications of Gauss's Law
Applications of Gauss's Law: Overview
This topic consists of various concepts like Electric Field due to a Long Line Charge Using Gauss's Law,Electric Field due to a Large Charged Sheet Using Gauss's Law,Electric Field due to a Charged Spherical Shell Using Gauss's Law, etc.
Important Questions on Applications of Gauss's Law
Applying Gauss theorem, the expression for the electric field intensity at a point due to an infinitely long, thin, uniformly charged straight wire is
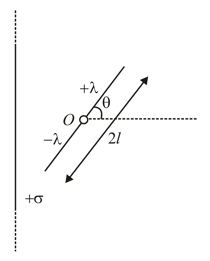
A thin infinite sheet charge and an infinite line charge of respective charge densities and are placed parallel at distance from each other. Points and are at and perpendicular distances from line charge towards sheet charge, respectively. and are the magnitudes of resultant electric field intensities at point and respectively. If for then the value of is _____.
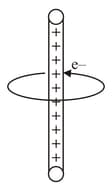
An electron revolves around an infinite cylindrical wire having uniform linear charge density in circular path under the influence of attractive electrostatic field as shown in the figure. The velocity of electron with which it is revolving is ______________ . Given mass of electron
Two identical infinite negative line charges are held along the lines in the plane. A charge- is placed at origin & is restricted to move along axis.Its equilibrium is
A positive charge q having mass , is released from rest in front of an infinite non-conducting sheet with surface charge density equal to . Speed of the charge particle after time is
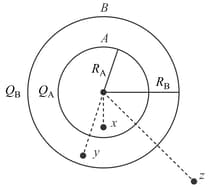
Consider an isolated, thin conducting spherical shell of radius . The shell is given a charge that distributes uniformly and due to only the maximum strength of the resulting electric field has a value due to only. is another isolated thin conducting spherical shell of radius . It is given a charge that distributes uniformly and in this case, maximum strength of the resulting field has a value due to only. The two shells and are now kept in a concentric manner as shown in figure. and are points as shown in figure, at distance from the centre, respectively. [Take at ]
Electric field at distance and from uniformly charged large non conducting sheet of surface charge density will be
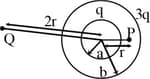
A thin square planar lamina is given a charge . A straight thin cylindrical conductor is kept parallel to the plane and given a charge . The length of the cylinder is also parallel to one of sides of the square lamina. The straight line joining the center of the plane and the center of the cylinder is perpendicular to the plane and also perpendicular to the geometric length of the cylinder. The distance is equal to the side length of the square lamina. It is observed that at the midpoint of the line the net electric field is zero. Assuming that the side length of the square is huge, calculate the ratio of charges . (Given that length of the cylinder is equal to the side length of the square plate)
The charge density of uniformly charged infinite plane is . A simple pendulum is suspended vertically downward near it. Charge is placed on metallic bob. If the angle made by the string is with vertical direction then _____
A hollow charged metal sphere has radius . If the potential difference between its surface and a point at a distance from the centre is, then electric field intensity at a distance is:
A parallel plate capacitor has two square plates with equal and opposite charges. The surface charge densities on the plates are and respectively. In the region between the plates the magnitude of the electric field is
The ratio of electric field intensity at & in the shown arrangement is
In the figure shown, there is a large sheet of charge of uniform surface charge density . A charge particle of charge and mass is projected from a point on the sheet with a speed with angle of projection such that it lands at maximum distance from on the sheet. Neglecting gravity, find the time of flight.
A conducting spherical shell of radius has a charge units. The electric field due to the shell at a point
A conducting spherical shell of radius has a charge units. The electric field due to the shell at a point
An electron is moving around an infinite linear charge in a circular path of diameter . If linear charge density is and the speed of the electron is written as, then find accurate up to two digits after the decimal point. (, )
solid conducting sphere of radius is enclosed by a thin metallic shell of radius charge of is given to the inner sphere. If the metallic shell is earthed, then the heat generated in the process is
A large sheet carries uniform surface charge density . A rod of length has a linear charge density on one half and on the second half. The rod is hinged at mid-point and makes an angle with the normal to the sheet. The electric force experienced by the rod is,
An electron of energy is fired from a distance of perpendicularly towards an infinite charged conducting plate. What should be the minimum charge density on plate so that electron fails to strike the plate?
A particle of mass is placed at some height above a uniformly charged horizontal infinite non conducting plate having a surface charge density . What should be the charge on the particle so that on releasing it will not fall down. Take,
