Basic Properties of Electric Charge
Basic Properties of Electric Charge: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as Additivity of Charges, Difference between Mass and Charge, Conservation of Electric Charges, Important Charged Particles, Proton, Electron, Quantization of Electric Charges, Invariance of Electric Charges, etc.
Important Questions on Basic Properties of Electric Charge
Two metallic spheres and of equal size each having charge and a third sphere of different size carries charge of . What will be the charge of sphere , if each of sphere and carries charge of after making contact between three spheres?
An electron at rest has a charge of . It starts moving with a velocity , where is the speed of light, then the new charge on it is-
If five charges are as follows , then what is total charge value?
For the addition of the charge, which one of the given things should be taken care of?
For the invariance of the charge, which of the given can be varied?
Out of gravitational, electrostatic, Van Der Waals and nuclear forces, which are able to provide attractive force between two neutrons
If an object has a net charge of , the number of excess electrons possessed by it is?
To give a charge of to some object, how many electrons are to be removed from it? ()
Which of the following statement is wrong?
Which Act allowed British officials to confiscate the property of Indian farmers?
Cotyledons are also called-
The number of electrons that must be removed from an electrically neutral silver dollar to give it a charge of is
Two identical spherical balls of diameter having charges and are brought in contact. After separation, the number of excess electrons on the first sphere is,
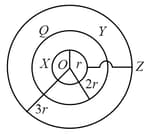
The concentric, conducting spherical shells and with radii and respectively. and are connected by a conducting wire and is uniformly charged to charge as shown in figure. Charges on shells and will be
If W is atomic weight and N is the atomic number of an element, then
The total positive charge in a glass of water containing of water is approximately:
Out of gravitational, electrostatic, Van der Waal and nuclear forces, which are able to provide attractive force between two neutrons?
Quantisation of charge implies
An - particle and a proton are subjected to the same electric field, then the ratio of the forces acting on them is
If an object has a net charge of , the number of excess electrons it possesses is
