Electromagnetic induction
Electromagnetic induction: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Electromagnetic Induction etc.
Important Questions on Electromagnetic induction
A coil of an area is placed in a magnetic field which changes from to in seconds. Find the induced e.m.f. in the coil.
Two identical co-axial loops carry a current ‘’ each circulating in the same direction. If loops approach each other then correct statement (s) is/are :
Magnetic flux linked with a stationary loop of resistance varies with time as . (In Wb). The amount of heat generated in joules during to is
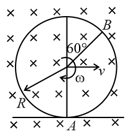
A conducting -shape rod is rotated with uniform angular speed in uniform magnetic field with the help of two equal string about an axis shown In the figure. Potential and is and respectively. (, magnetic field ) ( is mid point of ) match the following ( is directed opposite to )
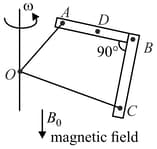
Two circular coils & are coaxially & carry currents and respectively (all direction are w.r.t. the observer)
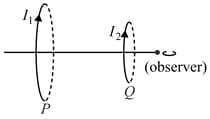
The diagram shows a circular non-conducting smooth fixed track kept concentric to a magnetic field of magnitude which exists in a cylindrical region of radius . There is small bead of mass and charge rests on the track. The bead can move freely along track. If the magnetic field is switched off then
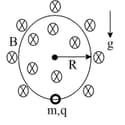
Uniform magnetic field present from to . A super conducting loop of given side length and self inductance start with speed with no initial current choose correct options. (Mass of loop is )
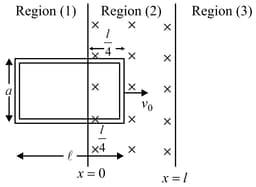
Two long parallel horizontal rails, a distance apart and each having a resistance per unit length, are joined at one end by a resistance . A perfectly conducting rod of mass is free to slide along the rails without friction (shown in figure). There is a uniform magnetic field of induction normal to the plane of the paper and directed into the paper. A variable force is applied to the rod such that, as the rod moves, a constant current I flows through . Let the applied force be expressed as function of the distance of the rod from , and be given by , where are functions of other variables. Find the exponent (power) of in the product .
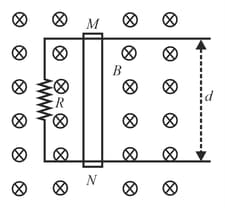
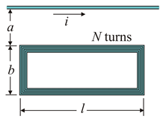
In the figure, a toroidal coil of a rectangular cross-section containing loops.
Its inner and outer radii are , respectively. The height of the torus is also
A thin conducting ring, encircles the turns, and carries a time dependent current,
Where and are constants and is resistance of coil.
A uniform disc of radius having charge distributed uniformly all over its surface is placed on a smooth horizontal surface. A magnetic field, , where is a constant is the distance (in metre) from the centre of the disc and is the time (in second), is switched on perpendicular to the plane of the disc. Find the torque (in ) acting on the disc after . (Take S.I. unit and ).
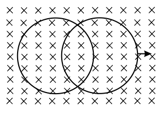
In the diagram shown, a uniform magnetic field is present perpendicular to the plane of the paper. Both the rings are identical and have a constant resistance per unit length. The left ring has been kept fixed at its position and the right ring is slide uniformly on the left ring towards the right hand side. Which of the following statements is/are true?
Will the earth’s magnetic field induce any current in the metallic surface of an artificial satellite when it is orbiting around the poles?
The primary winding of transformer has turns whereas its secondary has 5000 turns. The primary is connected to an ac supply of The secondary will have an output of :-
If a coil of metal wire is kept stationary in a uniform magnetic field, then _____.
The law of electromagnetic induction has been used in the construction of
Consider the given case
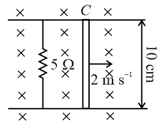
Magnetic field of is applied to this arrangement. If connecting wires and rod have negligible resistance. Then, the current through resistor is .
In the figure, a turn coil of radius and resistance is wrapped around a long solenoid of and diameter The axis of the coil and the axis of the solenoid make angle of with each other. The solenoid current drops from to zero in time interval Find the total charge that flows through the coil. Take
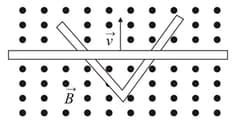
In the figure, two straight conducting rails form a right angle. A conducting bar in contact with the rails starts at the vertex at time and moves with a constant velocity of along them. A magnetic field is directed out of the page. The current in the loop is resistance per unit length of the rails and bar).
A rectangular loop of closely packed turns is positioned near a long straight wire as shown in figure. The rectangular loop performs linear with its distance varying as: where or The induced in the loop has the peak value.
A conducting whee of radius is rolling with angular speed on the ground in a uniform magnetic field then the emf induced between points and ; will be